TITLE 9. ENVIRONMENT
REGISTRAR'S NOTICE: The
following regulatory action is exempt from Article 2 of the Administrative
Process Act in accordance with § 2.2-4006 A 4 c of the Code of Virginia,
which excludes regulations that are necessary to meet the requirements of
federal law or regulations provided such regulations do not differ materially
from those required by federal law or regulation. The Virginia Waste Management
Board is also claiming an exemption from the Administrative Process Act in
accordance with § 2.2-4006 A 3 of the Code of Virginia, which excludes
regulations that consist only of changes in style or form or corrections of
technical errors. The Virginia Waste Management Board will receive, consider,
and respond to petitions by any interested person at any time with respect to
reconsideration or revision.
Title of Regulation: 9VAC20-60. Virginia Hazardous
Waste Management Regulations (amending 9VAC20-60-17, 9VAC20-60-18,
9VAC20-60-260 through 9VAC20-60-265, 9VAC20-60-268, 9VAC20-60-270, 9VAC20-60-273).
Statutory Authority: § 10.1-1402 of the Code of
Virginia; 42 USC § 6921 et seq.; 40 CFR Parts 260 through 272.
Effective Date: April 8, 2018.
Agency Contact: Lisa Ellis, Hazardous Waste Compliance
Coordinator, Department of Environmental Quality, 1111 East Main Street, Suite
1400, P.O. Box 1105, Richmond, VA 23218, telephone (804) 698-4237, or email
lisa.ellis@deq.virginia.gov.
Summary:
In this regulatory action, the Virginia Waste Management
Board incorporates Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations as published on
July 1, 2017, and adopts two final rules of the U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency (EPA) published in the Federal Register on November 28, 2016: Hazardous
Waste Export-Import Revisions and Hazardous Waste Generator Improvements Rule.
The hazardous waste export-import final rule (i) makes
existing export and import-related requirements more consistent with the
current import-export requirements for shipments between members of the
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, (ii) enables electronic
submittal to the EPA of all export and import-related documents, and (iii)
enables electronic validation of consent in the Automated Export System for
export shipments subject to Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
export consent requirements prior to exit.
The hazardous waste generator improvements final rule (i)
reorganizes the hazardous waste generator regulations to be more user friendly,
(ii) improves understanding of how the RCRA hazardous waste generator
regulatory program works, (iii) addresses gaps in the existing regulations to
strengthen environmental protection, (iv) provides greater flexibility for
hazardous waste generators to manage their hazardous waste in a cost-effective
and protective manner, and (v) makes technical corrections and conforming
changes to address inadvertent errors and remove obsolete references to
programs that no longer exist.
Other amendments update or correct citations and make other
technical corrections.
9VAC20-60-17. Definitions created by these regulations.
A. The following words and terms when used in this chapter
shall have the following meanings unless the context clearly indicates
otherwise:
"Administrator" means the Administrator of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency or his designee. See 9VAC20-60-14
B 1.
"Another regulation of the Virginia Administrative
Code" means any regulation that is not in 9VAC20-60, the Virginia
Hazardous Waste Management Regulations.
"Application, Part A" means that part of the
application that a permit applicant shall complete to qualify for interim
status under § 3005(e) of RCRA or this chapter and for consideration for a
permit.
"Application, Part B" means that part of the
application that a permit applicant shall complete to be considered for a
permit as required by 9VAC20-60-1010 9VAC20-60-270.
"Approved program" means a state program that has
been approved by the U.S. EPA. An "approved state" is one
administering an "approved program" under the hazardous waste management
provisions of RCRA.
"Authorization (authorized program)" means a state
hazardous waste program that has been approved under the authorities of RCRA.
"Authorized representative" means the manager,
superintendent, or person of equivalent responsibility responsible for the
overall operation of a facility or an operational unit (i.e., part of a
facility).
"Board" means the Virginia Waste Management Board.
"Commonwealth" means the Commonwealth of Virginia.
"Department" means the Virginia Department of Environmental
Quality.
"Director" means the Director of the Department of
Environmental Quality.
"Emergency permit" means a permit issued where an
imminent and substantial endangerment to human health or the environment is
determined to exist by the director.
"EPA" means the U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency. See 9VAC20-60-14 B 2.
"EPA identification number" means the number
assigned by EPA or the department to each hazardous waste generator, hazardous
waste transporter, or hazardous waste facility.
"EPA hazardous waste number" means the number
assigned by EPA to each waste listed in Subpart D of 40 CFR Part 261 and to
each waste exhibiting a characteristic identified in Subpart C of 40 CFR Part
261.
"Hazardous material" means a substance or material
which has been determined by the Secretary of Transportation to be capable of
posing an unreasonable risk to health, safety, and property when transported in
commerce, and which has been so designated under 49 CFR Parts 171 and 173.
"HSWA" means the Hazardous and Solid Waste
Amendments of 1984 (P.L. 98-616).
"HSWA drip pad" means a drip pad where F032 wastes
are handled.
"HSWA tank" means a tank owned or operated by a
small quantity generator or an underground tank for which construction
commenced after July 14, 1986, or an underground tank that cannot be entered
for inspection.
"HWM" means hazardous waste management.
"Non-HSWA tank" means any tank that is not a HSWA
tank.
"Non-HSWA drip pad" means a drip pad where F034 or
F035 wastes are handled.
"Permit" means a control document issued by the
Commonwealth pursuant to this chapter, or by the EPA administrator pursuant to
applicable federal regulations. The term "permit" includes any
functional equivalent such as an authorization, license, emergency permit, or
permit by rule. It does not include interim status under RCRA or this chapter,
nor does it include draft permits.
"Permitted hazardous waste management facility" or
"permitted facility" means a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or
disposal facility that has received an EPA or Commonwealth permit in accordance
with the requirements of this chapter or a permit from an authorized state
program.
"Qualified engineer" or "engineer" means
a professional engineer certified to practice in the Commonwealth of Virginia.
"RCRA" means the Solid Waste Disposal Act, as
amended by the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976 (42 USC § 6901 et
seq.).
"Regulation" means the control, direction and
governance of solid and hazardous waste activities by means of the adoption and
enforcement of laws, ordinances, rules and regulations.
"Responsible individual" means an individual
authorized to sign official documents for and act on behalf of a company or
organization. See also "authorized representative."
"Signature" means the name of a person written with
his own hand.
"State director" means the Director of the
Department of Environmental Quality.
"These regulations" means 9VAC20-60, the Virginia
Hazardous Waste Management Regulations.
"VHWMR" means 9VAC20-60, the Virginia Hazardous
Waste Management Regulations.
B. Terms used in liability insurance requirements. In the
liability insurance requirements, the terms "bodily injury" and
"property damage" shall have the meanings given these terms by the
case law of the Virginia court system. However, these terms do not include
those liabilities which, consistent with standard industry practices, are
excluded from coverage in liability policies for bodily injury and property
damage. The department intends the meanings of other terms used in the
liability insurance requirements to be consistent with their common meanings
within the insurance industry.
9VAC20-60-18. Applicability of incorporated references based on
the dates on which they became effective.
Except as noted, when a regulation of the United States
Environmental Protection Agency set forth in Title 40 of the Code of Federal
Regulations is referenced and incorporated herein, that regulation shall be as
it exists and has been published in the July 1, 2015 2017,
update.
9VAC20-60-260. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 260 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 260 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials, and other ancillaries that are a part of 40 CFR Part 260 are
also hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part 260 is incorporated by reference,
the following additions, modifications, and exceptions shall amend the
incorporated text for the purpose of its incorporation into these regulations:
1. In 40 CFR 260.10, the term "Administrator" shall
mean the administrator Administrator of the United States
Environmental Protection Agency or his designee.
2. In 40 CFR 260.10, the term "contained" shall be
appended by adding the following: (5) Hazardous secondary materials managed
under the exclusion provided in 40 CFR 261.4(a)(23) or (a)(24) shall not be
managed in a land-based unit unless the land-based unit meets the applicable
standards of 40 CFR Parts 260 through 270, as incorporated by reference, for management
of hazardous waste.
3. In 40 CFR 260.10, the term "EPA" shall mean the
United States Environmental Protection Agency.
4. In 40 CFR 260.10 the term "new tank system" and
"existing tank system," the reference to July 14, 1986, applies only
to tank regulations promulgated pursuant to federal Hazardous and Solid Waste
Amendment (HSWA) requirements. HSWA requirement categories include:
a. Interim status and permitting requirements applicable to
tank systems owned and operated by small quantity generators;
b. Leak detection requirements for all underground tank
systems for which construction commenced after July 14, 1986; and
c. Permitting standards for underground tanks that cannot be
entered for inspection.
For non-HSWA regulations, the reference date shall be January
1, 1998.
5. In 40 CFR 260.10, the term "Regional
Administrator" shall mean the regional administrator Regional
Administrator of Region III of the United States Environmental Protection
Agency or his designee.
6. In 40 CFR 260.10 definitions of the terms
"Person," "State," and "United States," the term
"state" shall have the meaning originally intended by the Code of
Federal Regulations and not be supplanted by "Commonwealth of Virginia."
7. In 40 CFR 260.10 and wherever elsewhere in Title 40 of the
Code of Federal Regulations the term "universal waste" appears, it
shall be amended by addition of the following sentence: "In addition to
the hazardous wastes listed herein, the term "universal waste" shall
include those hazardous wastes listed in Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et seq.) of
the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations as universal wastes, under
such terms and requirements as shall therein be ascribed."
8. Throughout 40 CFR 260.11(a), the terms "EPA" and
"U.S. Environmental Protection Agency" shall not be supplanted with
the term "Commonwealth of Virginia."
9. In Part XIV (9VAC20-60-1370 et seq.), the Virginia
Hazardous Waste Management Regulations contain provisions analogous to 40 CFR
260.30, 40 CFR 260.31, 40 CFR 260.32,
40 CFR 260.33, 40 CFR 260.34, 40 CFR
260.40, and 40 CFR 260.41. These sections of 40 CFR Part 260 are not
incorporated by reference and are not a part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste
Management Regulations.
10. Sections 40 CFR 260.2, 40 CFR 260.20, 40 CFR 260.21, 40 CFR 260.22, and 40 CFR
260.23 are not included in the incorporation of 40 CFR Part 260 by reference
and are not a part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations.
11. Appendix I to 40 CFR Part 260 is not incorporated by
reference and is not a part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
12. In the 40 CFR 260.10 definitions of the terms "AES
filing compliance date," and "Electronic import-export reporting
compliance date," the term "EPA" shall have the meaning originally
intended by the Code of Federal Regulations and not be supplanted by
"Department of Environmental Quality."
9VAC20-60-261. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 261 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 261 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials, and other ancillaries that are a part of 40 CFR Part 261 are also
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
261 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications, and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. Any agreements required by 40 CFR 261.4(b)(11)(ii) shall be
sent to the United States Environmental Protection Agency at the address shown
and to the Department of Environmental Quality, P.O. Box 1105, Richmond,
Virginia 23218.
2. In 40 CFR 261.4(e)(3)(iii), the text "in the Region
where the sample is collected" shall be deleted.
3. In 40 CFR 261.4(f)(1), the term "Regional
Administrator" shall mean the regional administrator Regional
Administrator of Region III of the United States Environmental Protection
Agency or his designee.
4. In 40 CFR 261.6(a)(2), recyclable materials shall be
subject to the requirements of 9VAC20-60-270 and Part XII (9VAC20-60-1260 et
seq.) of this chapter.
5. No hazardous waste from a conditionally exempt small
quantity generator shall be managed as described in 40 CFR 261.5(g)(3)(iv) or 40 CFR
261.5(g)(3)(v) unless such waste management is in full compliance with all
requirements of the Solid Waste Management Regulations (9VAC20-81) Reserved.
6. In 40 CFR 261.9 and wherever elsewhere in Title 40 of the
Code of Federal Regulations there is a listing of universal wastes or a listing
of hazardous wastes that are the subject of provisions set out in 40 CFR Part
273 as universal wastes, it shall be amended by addition of the following
sentence: "In addition to the hazardous wastes listed here, the term
"universal waste" and all lists of universal waste or waste subject
to provisions of 40 CFR Part 273 shall include those hazardous wastes listed in
Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et seq.) of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations as universal wastes, in accordance with the terms and requirements
described."
7. In Subparts B and D of 40 CFR Part 261, the term
"Administrator" shall mean the administrator Administrator
of the United States Environmental Protection Agency, and the term
"Director" shall not supplant "Administrator" throughout
Subparts B and D.
8. For the purpose of this chapter, any solid waste is a
hazardous waste if it is defined to be hazardous waste under the laws or
regulations of the state in which it first became a solid waste.
9. In 40 CFR 261.6(c)(1) and 40 CFR 261.6(c)(2)
mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities must also comply with all
applicable requirements of 9VAC20-60-264 B 34 and 9VAC20-60-265 B 21.
10. In Subpart E of 40 CFR Part 261, the term
"EPA" shall have the meaning originally intended by the Code of
Federal Regulations and not be supplanted by "Department of Environmental
Quality."
11. In 40 CFR 261.2(a), reference to 40 CFR 260.30, 40 CFR 260.31, and 40 CFR 260.34 are replaced
by analogous provisions of Part XIV (9VAC20-60-1370 et seq.) of this chapter
12. In 40 CFR 261.3(a)(2), reference to exclusion under 40 CFR 260.20 and 40 CFR 260.22 are not
incorporated by reference.
9VAC20-60-262. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 262 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 262 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials, and other ancillaries that are parts of 40 CFR Part 262 are also
hereby incorporated as parts of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
262 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications, and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. In 40 CFR 262.42(a)(2), the words "for the Region in
which the generator is located" is deleted from the incorporated text and
is not a part of these regulations.
2. In 40 CFR 262.12, 40 CFR 262.53, 40 CFR 262.54,
40 CFR 262.55, 40 CFR 262.56,
and 40 CFR 262.57 262.18 and 40 CFR 262 Subpart H, the term
"Administrator" shall mean the administrator Administrator
of the United States Environmental Protection Agency or his designee.
3. In 40 CFR 262.12, 40 CFR 262.53, 40 CFR 262.54,
40 CFR 262.55, 40 CFR 262.56,
and 40 CFR 262.57, 262.18 and 40 CFR 262 Subpart H, the term
"Regional Administrator" shall mean the regional administrator
Regional Administrator of Region III of the United States Environmental
Protection Agency or his designee.
4. For accumulation areas established before March 1, 1988,
all large quantity generators shall notify the department of each location
where he accumulates hazardous waste in accordance with 40 CFR 262.34 by March
1, 1988. For accumulation areas established after March 1, 1988, he a
large quantity generator shall notify the department and document in the
operating record that he intends to accumulate hazardous waste in accordance
with 40 CFR 262.34 262.17 prior to or immediately upon the
establishment of each 90-day accumulation area. In the case of a new large
quantity generator who creates such accumulation areas after March 1, 1988, he
shall notify the department at the time the generator files the Notification of
Hazardous Waste Activity EPA Form 8700-12 that he intends to
accumulate hazardous waste in accordance with 40 CFR
262.34 262.18. This notification shall specify the exact location
of the 90-day accumulation area at the site.
5. In addition to the requirements in 40 CFR Part 262,
management of hazardous wastes is required to comply with the Regulations
Governing the Transportation of Hazardous Materials (9VAC20-110), including
packaging and labeling for transport.
6. A generator shall not offer his hazardous waste to a
transporter that has not received an EPA identification number or to a facility
that has not received a permit and an EPA identification number.
7. In 40 CFR 262.24, 40 CFR 262.25, and 40 CFR Part 262,
Subpart H, the terms "EPA" and "Environmental Protection
Agency" shall mean the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
8. In addition to the requirements of this section, large
quantity generators are required to pay an annual fee. The fee schedule and fee
regulations are contained in Part XII (9VAC20-60-1260 through 9VAC20-60-1286)
of this chapter.
9. Within 40 CFR 262.24, the reference to "system"
means the United States Environmental Protection Agency's national electronic
manifest system.
10. Regardless of the provisions of 9VAC20-60-18, the
requirements of 40 CFR 262.24(g) are not incorporated into this chapter.
11. In 40 CFR 262.11(c) and 40 CFR 262.11(d), the term
"Administrator" shall mean the Administrator of the United States
Environmental Protection Agency.
12. No hazardous waste from a very small quantity generator
shall be managed as described in 40 CFR 262.14(a)(5)(iv) or 40 CFR
262.14(a)(5)(v) unless such waste management is in full compliance with all
requirements of the Solid Waste Management Regulations (9VAC20-81).
13. In 40 CFR 262 Subpart H, the term
"Administrator" shall mean the Administrator of the United States
Environmental Protection Agency.
9VAC20-60-263. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 263 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 263 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials, and other ancillaries that are parts of 40 CFR Part 263 are also
hereby incorporated as parts of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
263 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications, and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. Additional requirements for transportation of hazardous
materials are included in Part VII (9VAC20-60-420 et seq.) of this chapter and
in the Regulations Governing the Transportation of Hazardous Materials
(9VAC20-110).
2. Sections of 40 CFR 263.10(d), 40 CFR 263.20(a)(2), 40 CFR 263.21(a)(2), 40 CFR 263.30, and
40 CFR 263.31 are not incorporated by reference and are not a part of the
Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations. See 9VAC20-60-490 for
requirements related to transportation discharge management.
3. In 40 CFR 263.20, the terms "EPA" and
"Environmental Protection Agency" shall mean the United States
Environmental Protection Agency, and the reference to "system" means
the United States Environmental Protection Agency's national electronic
manifest system.
4. Regardless of the provisions of 9VAC20-60-18, the
requirements of 40 CFR 263.20(a)(8) are not incorporated into this chapter.
9VAC20-60-264. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 264 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 264 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials and other ancillaries that are a part of 40 CFR Part 264 are also
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
264 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications, and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. Sections 40 CFR 264.1(d), 40 CFR 264.1(f), 40 CFR
264.149, 40 CFR 264.150, 40 CFR 264.301(l), and Appendix VI are not included in
the incorporation of 40 CFR Part 264 by reference and are not a part of
the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations.
2. In 40 CFR 264.1(g)(11) and wherever elsewhere in Title 40
of the Code of Federal Regulations there is a listing of universal wastes or a
listing of hazardous wastes that are the subject of provisions set out in 40
CFR Part 273 as universal wastes, it shall be amended by addition of the
following sentence: "In addition to the hazardous wastes listed here, the
term "universal waste" and all lists of universal waste or waste
subject to provisions of 40 CFR Part 273 shall include those hazardous
wastes listed in Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et seq.) of the Virginia Hazardous
Waste Management Regulations as universal wastes, in accordance with the terms
and requirements described."
3. In 40 CFR 264.12(a), the term "Regional
Administrator" shall mean the regional administrator Regional
Administrator of Region III of the United States Environmental Protection
Agency or his designee.
4. In 40 CFR 264.33, the following sentence shall be added to
the end of the paragraph: "A record of tests or inspections will be maintained
on a log at that facility or other reasonably accessible and convenient
location."
5. In addition to the notifications required by 40 CFR
264.56(d)(2), notification shall be made to the on-scene coordinator, the
National Response Center, and the Virginia Department of Emergency Management,
Emergency Operations Center. In the associated report filed under 40 CFR 264.56(j)
264.56(i), the owner or operator shall include such other information
specifically requested by the director, which is reasonably necessary and
relevant to the purpose of an operating record.
6. In 40 CFR 264.93, "hazardous constituents" shall
include constituents identified in 40 CFR Part 264 Appendix IX in addition to
those in 40 CFR Part 261 Appendix VIII.
7. The federal text at 40 CFR 264.94(a)(2) is not incorporated
by reference. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR 264.94(a)(2):
"For any of the constituents for which the USEPA has established a Maximum
Contaminant Level (MCL) under the National Primary Drinking Water Regulation,
40 CFR Part 141 (regulations under the Safe Drinking Water Act), the
concentration must not exceed the value of the MCL; or if the background
level of the constituent is below the MCL; or."
8. The owner or operator must submit the detailed, written
closure cost estimate described in 40 CFR 264.142 upon the written request of
the director.
9. In 40 CFR 264.143(b)(1), 40 CFR 264.143(c)(1), 40 CFR
264.145(b)(1), and 40 CFR 264.145(c)(1), any surety company issuing
surety bonds to guarantee payment or performance must be licensed pursuant to
Chapter 10 (§ 38.2-1000 et seq.) of Title 38.2 of the Code of Virginia.
10. In 40 CFR 264.143(b), 40 CFR 264.143(c), 40 CFR 264.145(b) and 40 CFR 264.145(c), any
owner or operator demonstrating financial assurance for closure or post-closure
care using a surety bond shall submit with the surety bond a copy of the deed
book page documenting that the power of attorney of the attorney-in-fact
executing the bond has been recorded pursuant to § 38.2-2416 of the Code
of Virginia.
11. Where in 40 CFR 264.143(c)(5) the phrase "final
administrative determination pursuant to section 3008 of RCRA" appears, it
shall be replaced with "final determination pursuant to Chapter 40 (§
2.2-4000 et seq.) of Title 2.2 of the Code of Virginia."
12. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
264.143(d)(8): "Following a final administrative determination pursuant to
Chapter 40 (§ 2.2-4000 et seq.) of Title 2.2 of the Code of Virginia that the
owner or operator has failed to perform final closure in accordance with the
approved closure plan, the applicable regulations or other permit requirements
when required to do so, the director may draw on the letter of credit."
13. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR 264.143(e)(1):
"An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by
obtaining closure insurance which conforms to the requirements of this
paragraph and submitting a certificate of such insurance, along with a complete
copy of the insurance policy, to the department. An owner or operator of a new
facility must submit the certificate of insurance along with a complete copy of
the insurance policy to the department at least 60 days before the date on
which the hazardous waste is first received for treatment, storage or disposal.
The insurance must be effective before this initial receipt of hazardous waste.
At a minimum, the insurer must be licensed pursuant to Chapter 10
(§ 38.2-1000 et seq.) of Title 38.2 of the Code of Virginia."
14. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR 264.143(f)(3)(ii), 40 CFR
264.145(f)(3)(ii) and 40 CFR
264.147(f)(3)(ii): "A copy of the owner's or operator's audited financial
statements for the latest completed fiscal year; including a copy of the
independent certified public accountant's report on examination of the owner's
or operator's financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year;
and"
15. In addition to the other requirements in 40 CFR
264.143(f)(3), 40 CFR 264.145(f)(3) and 40 CFR 264.147(f)(3), an owner or
operator must submit confirmation from the rating service that the owner or
operator has a current rating for its most recent bond issuance of AAA, AA, A,
or BBB as issued by Standard and Poor's or Aaa, Aa, A, or Baa as issued by
Moody's if the owner or operator passes the financial test with a bond rating
as provided in 40 CFR 264.143(f)(1)(ii)(A).
16. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
264.143(h) and 40 CFR 264.145(h): "An owner or operator may use a
financial assurance mechanism specified in this section to meet the
requirements of this section for more than one facility in Virginia. Evidence
of financial assurance submitted to the department must include a list showing,
for each facility, the EPA Identification Number, name, address, and the amount
of funds for closure or post-closure assured by the mechanism. The amount of
funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds
that would be available if a separate mechanism had been established and
maintained for each facility. In directing funds available through the
mechanism for closure or post-closure care of any of the facilities covered by
the mechanism, the director may direct only the amount of funds designated for
that facility, unless the owner or operator agrees to the use of additional
funds available under the mechanism."
17. In addition to the requirements of 40 CFR 264.144, "the owner or operator
must submit a detailed, written post-closure cost estimate upon the written
request of the director."
18. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
264.144(b): "During the active life of the facility and the post-closure
period, the owner or operator must adjust the post-closure cost estimate for
inflation within 60 days prior to the anniversary date of the establishment of
the financial instrument(s) instruments used to comply with 40 CFR
264.145. For owners or operators using the financial test or corporate
guarantee, the post-closure cost estimate must be updated for inflation within
30 days after the close of the firm's fiscal year and before the submission of
updated information to the department as specified in 40 CFR
264.145(f)(5). The adjustment may be made by recalculating the post-closure
cost estimate in current dollars or by using an inflation factor derived from
the most recent Implicit Price Deflator for Gross National Product published by
the U.S. Department of Commerce in its Survey of Current Business as specified
in 40 CFR 264.142(b)(1) and (2). The inflation factor is the result of
dividing the latest published annual Deflator by the Deflator for the previous
year.
a. The first adjustment is made by multiplying the
post-closure cost estimate by the inflation factor. The result is the adjusted
post-closure cost estimate.
b. Subsequent adjustments are made by multiplying the latest
adjusted post-closure cost estimate by the latest inflation factor."
19. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
264.144(c): "During the active life of the facility and the post-closure
period, the owner or operator must revise the post-closure cost estimate within
30 days after the director has approved the request to modify the post-closure
plan, if the change in the post-closure plan increases the cost of post-closure
care. The revised post-closure cost estimate must be adjusted for inflation as
specified in 264.144(b)."
20. Where in 40 CFR 264.145(c)(5) the phrase "final
administrative determination pursuant to section 3008 of RCRA" appears, it
shall be replaced with "final determination pursuant to Chapter 40 (§
2.2-4000 et seq.) of Title 2.2 of the Code of Virginia."
21. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
264.145(d)(9): "Following a final administrative determination pursuant to
Chapter 40 (§ 2.2-4000 et seq.) of Title 2.2 of the Code of Virginia that the
owner or operator has failed to perform post-closure in accordance with the
approved post-closure plan, the applicable regulations, or other permit
requirements when required to do so, the director may draw on the letter of
credit."
22. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
264.145(e)(1): "An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this
section by obtaining post-closure insurance which conforms to the requirements
of this paragraph and submitting a certificate of such insurance to the
department. An owner or operator of a new facility must submit the certificate
of insurance along with a complete copy of the insurance policy to the
department at least 60 days before the date on which the hazardous waste is
first received for treatment, storage or disposal. The insurance must be
effective before this initial receipt of hazardous waste. At a minimum, the
insurer must be licensed pursuant to Chapter 10 (§ 38.2-1000 et seq.) of
Title 38.2 of the Code of Virginia."
23. In 40 CFR 264.147(a)(1)(ii), 40 CFR 264.147(b)(1)(ii), 40 CFR 264.147(g)(2), and 40 CFR
264.147(i)(4), the term "Virginia" shall not be substituted for the
term "State" or "States."
24. In 40 CFR 264.191(a), the compliance date of January 12,
1988, applies only for HSWA tanks. For non-HSWA tanks, the compliance date is
November 2, 1997, instead of January 12, 1997.
25. In 40 CFR 264.191(c), the reference to July 14, 1986,
applies only to HSWA tanks. For non-HSWA tanks, the applicable date is November
2, 1987, instead of July 14, 1986.
26. In 40 CFR 264.193, the federal effective dates apply only
to HSWA tanks. For non-HSWA tanks, the applicable date is November 2, 1997,
instead of January 12, 1997.
27. A copy of all reports made in accordance with 40 CFR
264.196(d) shall be sent to the director and to the chief administrative
officer of the local government of the jurisdiction in which the event occurs.
The sentence in 40 CFR 264.196(d)(1), "If the release has been
reported pursuant to 40 CFR Part 302, that report will satisfy this
requirement." is not incorporated by reference into these regulations and
is not a part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations.
28. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR 264.570(a):
"The requirements of this subpart apply to owners and operators of
facilities that use new or existing drip pads to convey wood drippage,
precipitation and/or surface water run-off to an associated collection system.
Existing HSWA drip pads are those constructed before December 6, 1990, and
those for which the owner or operator has a design and has entered into a
binding financial or other agreement for construction prior to December 6,
1990. Existing non-HSWA drip pads are those constructed before January 14,
1993, and those for which the owner or operator has a design and has entered
into a binding financial or other agreements for construction prior to January
14, 1993. All other drip pads are new drip pads. The requirement at 40 CFR
264.573(b)(3) to install a leak collection system applies only to those HSWA
drip pads that are constructed after December 24, 1992, except for those
constructed after December 24, 1992, for which the owner or operator has a
design and has entered into a binding financial or other agreement for
construction prior to December 24, 1992. For non-HSWA drip pads, the
requirement at 40 CFR 264.573(b)(3) to install a leak collection system
applies only to those non-HSWA drip pads that are constructed after September
8, 1993, except for those constructed after September 8, 1993, for which the
owner or operator has a design and has entered into a binding financial or
other agreement for construction prior to September 8, 1993."
29. In 40 CFR 264.1030(c), the reference to 40 CFR 124.15
shall be replaced by a reference to 40 CFR 124.5.
30. The underground injection of hazardous waste for
treatment, storage or disposal shall be prohibited throughout the Commonwealth
of Virginia.
31. In addition to the notices required in Subpart B and
others parts of 40 CFR Part 264, the following notices are also required:
a. The owner or operator of a facility that has arranged to
receive hazardous waste from a foreign source (a source located outside of the
United States of America) shall notify the department and administrator in
writing at least four weeks in advance of the date the waste is expected to
arrive at the facility. Notice of subsequent shipments of the same waste from
the same foreign source is not required.
b. The owner or operator of a facility that receives hazardous
waste from an off-site source (except where the owner or operator of the
facility is also the generator of this waste) shall inform the generator in
writing that he has appropriate permits for, and will accept, the waste that
the generator is shipping. The owner or operator shall keep a copy of this
written notice as part of the operating record.
c. Before transferring ownership or operation of a facility
during its operating life, or of a disposal facility during the post-closure
care period, the owner or operator shall notify the new owner or operator in
writing of the requirements contained in this section and 9VAC20-60-270. An
owner or operator's failure to notify the new owner or operator of the above
requirements in this section and 9VAC20-60-270 in no way relieves the
new owner or operator of his obligation to comply with all applicable
requirements.
d. Any person responsible for the release of a hazardous
substance from the facility that poses an immediate or imminent threat to
public health and who is required by law to notify the National Response Center
shall notify the department and the chief administrative officer of the local
government of the jurisdiction in which the release occurs or their designees.
In cases when the released hazardous substances are hazardous wastes or
hazardous waste constituents additional requirements are prescribed by Subpart
D of 40 CFR Part 264.
32. In 40 CFR 264.71, the terms "EPA" and
"Environmental Protection Agency" shall mean the United States
Environmental Protection Agency, and the reference to "system" means
the United States Environmental Protection Agency's national electronic
manifest system.
33. Regardless of the provisions of 9VAC20-60-18, the
requirements of 40 CFR 264.71(j) are not incorporated into this chapter.
34. Requirements for mercury-containing lamp recycling
facilities. The following requirements apply to all facilities that recover or
reclaim mercury from lamps.
a. All owners and operators of mercury-containing lamp
recycling facilities shall:
(1) Have established markets for the utilization of reclaimed
materials and be able to identify these markets to the department;
(2) Only introduce into the processing equipment lamps or
devices for which the equipment was specifically designed to process and
operate and maintain processing equipment consistent with the equipment
manufacturer's specifications; and
(3) Not speculatively accumulate the materials.
b. If a mercury-containing lamp recycling facility's
processed materials are to be delivered to a facility other than a mercury
reclamation facility, the owner or operator shall:
(1) Demonstrate proper equipment operation and efficiency
by sampling and analytical testing of the processed materials. The testing
shall ensure that such processed materials (i) have less than three parts per
million of "average mercury" during each consecutive 12-week time
period of operations ("average mercury" shall be calculated pursuant
to subdivision 34 b (3) of this subsection); (ii) have less than five parts per
million of total mercury as reported in the "weekly composite sample of
process operations" ("weekly composite sample of process
operations" shall be calculated pursuant to subdivision 34 b (3) of this
subsection); (iii) are not a hazardous waste; and (iv) comply with 40 CFR Part 268, if applicable.
(2) Retest, reprocess, or deliver to a mercury reclamation
facility processed materials that are in excess of the allowable levels of
mercury specified in subdivision 34 b (1) of this subsection.
(3) Sample and perform analytical testing of the processed
material for total mercury as follows:
(a) Facility operators shall take daily physical samples of
the mercury-containing materials at the point at which they exit the processing
equipment. These samples shall be representative of the materials
processed during that day.
(b) At the beginning of each week, the prior week's daily
samples shall be consolidated into one weekly sample, which shall be submitted
for chemical analysis of total mercury content using an approved EPA
methodology. At least three separate daily samples shall be taken in order to
obtain a weekly sample. When a facility is not operating at least three days
during a week, that week will be dropped out of the 12-week rolling average as
calculated under subdivision 34 b (3) (c) of this subsection. However, all
daily samples that are in a week that has been dropped out shall be counted
towards the very next weekly sample that is included in a 12-week rolling average.
The result of this analysis shall be considered the "weekly composite
sample of process operations."
(c) The "average mercury" value calculation shall be
the rolling average of weekly composite sample results from samples taken
during the most recent 12-week time period with each new weekly composite
sample result replacing the oldest sample result that was used in the previous
12-week period.
c. Mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities shall ensure
that the separated materials that are generated from their operations are
suitable and safe for their intended end use and shall bear the burden of
responsibility for the safety of these materials sold or delivered from the
operations. Facilities shall notify in writing receiving sources, other than mercury
reclamation facilities, of the amount and type of hazardous substances present
in the processed materials as demonstrated by laboratory analysis.
d. Operating requirements. Mercury-containing lamp recycling
facilities shall be operated in accordance with the following requirements:
(1) Mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities shall control
mercury emissions through the use of a single air handling system with
redundant mercury controls and comply with the following:
(a) The owner or operator shall operate, monitor, and maintain
an air handling system with redundant air pollution control equipment in order
to reduce the mercury content of the air collected during the volume reduction
and mercury recovery and reclamation processes.
(b) Redundant air pollution control equipment shall
incorporate at least two carbon filters or equivalent technology arranged in a
series so that the air passes through both filters before being released. In
the event of a single filter failure, each filter shall be designed to ensure
compliance with the risk-based protectiveness standards for mercury vapor
provided in subdivision 34 e of this subsection.
(c) A sample of air shall be collected after the first carbon
filter (or equivalent technology) and upstream of the second once each
operating day while mercury-containing lamps or devices are being processed.
The mercury content of the sample shall be determined for comparison with the
risk-based protectiveness standards provided in subdivision 34 e of this
subsection.
(d) The owner or operator shall operate, monitor, and maintain
the air pollution control equipment in such a manner as not to exceed the
risk-based protectiveness standards under subdivision 34 e of this subsection
for mercury vapor downstream of the first carbon filter (or equivalent
technology) and upstream of the second carbon filter.
(2) The area in which the processing equipment is located
shall be fully enclosed and kept under negative pressure while processing
mercury-containing lamps or devices.
e. Testing for mercury releases from lamp crushing units shall
be performed using a mercury vapor analyzer that has been approved for the
application by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration or the
Virginia Department of Labor and Industry or a comparable device that has been
calibrated by the manufacturer or laboratory providing the equipment. Mercury
vapor monitors used for testing must be capable of detecting mercury at the
applicable concentrations provided below or lower in air and must be equipped
with a data recording device to provide a record of measurements taken. Mercury
monitoring data shall be documented and available for inspection in accordance
with subdivision 34 g of this subsection. The acute exposure protectiveness
standard is 300 µg/m3 for a 10-minute exposure with the
understanding that the acute exposure protectiveness standard is considered a
ceiling value and at no time during bulb crushing operation will the air
concentrations of mercury exceed 300 µg/m3. The following are
risk-based protectiveness standards at a distance of five feet from the bulb
crushing unit:
|
Monthly Bulb Crushing Duration
(X Hours/Month)*
|
Chronic Exposure Air Emission
Limit (µg/m3)
|
Acute Exposure Air Emission
Limit (µg/m3)
|
|
X = 32
|
1.314skin µg/m3
|
300 µg/m3
|
|
8 < X < 32
|
6.317 skin µg/m3
|
300 µg/m3
|
|
X = 8
|
27.375 skin µg/m3
|
300 µg/m3
|
|
*Monthly crushing duration is determined based on the
maximum number of hours that bulb crushing occurred in any one month over the
last 12-month period.
|
f. Closure. Mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities must
prepare and maintain a closure plan conforming to the requirements of 40 CFR
Part 264, Subpart G as adopted by reference in this section. Financial
assurance shall be provided to the department in accordance with 40 CFR Part
264, Subpart H as adopted by reference in this section.
g. Recordkeeping requirements. The owner or operator of a
mercury-containing lamp recycling facility shall maintain records of monitoring
information that (i) specify the date, place, and time of measurement; (ii)
provide the methodology used; and (iii) list the analytical results. The
records maintained shall include all calibration and maintenance records of
monitoring equipment. The owner or operator shall retain records of all
monitoring data and supporting information available for department inspection
for a period of at least three years from the date of collection.
35. The following additional information is required from
owners or operators of facilities that store or treat hazardous waste in waste
piles if an exemption is sought to Subpart F of 40 CFR Part 264 and 40 CFR
264.251 as provided in 40 CFR 264.250(c) and 40 CFR 264.90(b)(2):
a. An explanation of how the standards of 40 CFR 264.250(c) will be complied with; and
b. Detailed plans and an engineering report describing how
the requirements of 40 CFR 264.90(b)(2) will be met.
9VAC20-60-265. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 265 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 265
are hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials and other ancillaries that are parts of 40 CFR Part 265 are also hereby incorporated as parts of the
Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
265 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications, and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. Sections 40 CFR 265.1(c)(4), 40 CFR 265.149 and 40 CFR
265.150 and Subpart R of 40 CFR Part 265 are not included in the incorporation
of 40 CFR Part 265 by reference and are not a part of the Virginia Hazardous
Waste Management Regulations.
2. In 40 CFR 265.1(c)(14) and wherever elsewhere in Title 40
of the Code of Federal Regulations there is a listing of universal wastes or a
listing of hazardous wastes that are the subject of provisions set out in 40
CFR Part 273 as universal wastes, it shall be amended by addition of the
following sentence: "In addition to the hazardous wastes listed here, the
term "universal waste" and all lists of universal waste or waste
subject to provision of 40 CFR Part
273 shall include those hazardous wastes listed in Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et
seq.) of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations as universal
wastes, in accordance with the terms and requirements described."
3. A copy of all reports and notices made in accordance with
40 CFR 265.12 shall be sent to the department, the administrator and the chief
administrative officer of the local government of the jurisdiction in which the
event occurs.
4. In 40 CFR 265.12(a), the term "Regional
Administrator" shall mean the regional administrator Regional
Administrator of Region III of the United States Environmental Protection
Agency or his designee.
5. In 40 CFR 265.33, the following sentence shall be added to
the end of the paragraph: "A record of tests or inspections will be
maintained on a log at that facility or other reasonably accessible and
convenient location."
6. In addition to the notifications required by 40 CFR
265.56(d)(2), notification shall be made to the on-scene coordinator, the
National Response Center, and the Virginia Department of Emergency Management,
Emergency Operations Center. In the associated report filed under 40 CFR 265.56(j)
265.56(i), the owner or operator shall include such other information
specifically requested by the director, which is reasonably necessary and
relevant to the purpose of an operating record.
7. In addition to the requirements of 40 CFR 265.91, a log
shall be made of each ground water monitoring well describing the soils or rock
encountered, the permeability of formations, and the cation exchange capacity
of soils encountered. A copy of the logs with appropriate maps shall be sent to
the department.
8. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
265.143(g) and 40 CFR 265.145(g): "An owner or operator may use a
financial assurance mechanism specified in this section to meet the
requirements of this section for more than one facility in Virginia. Evidence
of financial assurance submitted to the department must include a list showing,
for each facility, the EPA Identification Number, name, address, and the amount
of funds for closure or post-closure assured by the mechanism. The amount of
funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds
that would be available if a separate mechanism had been established and
maintained for each facility. In directing funds available through the
mechanism for closure or post-closure care of any of the facilities covered by
the mechanism, the director may direct only the amount of funds designated for
that facility, unless the owner or operator agrees to the use of additional
funds available under the mechanism.
9. In 40 CFR 265.147(a)(1)(ii), 40 CFR 265.147(g)(2), and 40
CFR 265.147(i)(4), the term "Virginia" shall not be substituted for
the term "State" or "States."
10. In 40 CFR 265.191(a), the compliance date of January 12,
1988, applies only for HSWA tanks. For non-HSWA tanks, the compliance date is
November 2, 1986.
11. In 40 CFR 265.191(c), the reference to July 14, 1986,
applies only to HSWA tanks. For non-HSWA tanks, the applicable date is November
2, 1987.
12. In 40 CFR 265.193, the federal effective dates apply only
to HSWA tanks. For non-HSWA tanks, the applicable date of January 12, 1987, is
replaced with November 2, 1997.
13. The following text shall be substituted for 40 CFR
265.440(a): "The requirements of this subpart apply to owners and
operators of facilities that use new or existing drip pads to convey wood
drippage, precipitation and/or surface water run-off to an associated
collection system. Existing HSWA drip pads are those constructed before
December 6, 1990, and those for which the owner or operator has a design and
has entered into a binding financial or other agreement for construction prior
to December 6, 1990. Existing non-HSWA drip pads are those constructed before
January 14, 1993, and those for which the owner or operator has a design and
has entered into a binding financial or other agreement for construction prior
to January 14, 1993. All other drip pads are new drip pads. The requirement at
40 CFR 265.443(b)(3) to install a leak collection system applies only to those
HSWA drip pads that are constructed after December 24, 1992, except for those
constructed after December 24, 1992, for which the owner or operator has a
design and has entered into a binding financial or other agreement for
construction prior to December 24, 1992. For non-HSWA drip pads, the
requirement at 40 CFR 264.573(b)(3) to install a leak collection system applies
only to those non-HSWA drip pads that are constructed after September 8, 1993,
except for those constructed after September 8, 1993, for which the owner or
operator has a design and has entered into a binding financial or other
agreement for construction prior to September 8, 1993."
14. In 40 CFR 265.1083(c)(4)(ii), the second occurrence of the
term "EPA" shall mean the United States Environmental Protection
Agency.
15. In addition to the requirements of 40 CFR 265.310, the
owner or operator shall consider at least the following factors in addressing
the closure and post-closure care objectives of this part:
a. Type and amount of hazardous waste and hazardous waste
constituents in the landfill;
b. The mobility and the expected rate of migration of the
hazardous waste and hazardous waste constituents;
c. Site location, topography, and surrounding land use, with
respect to the potential effects of pollutant migration;
d. Climate, including amount, frequency and pH of
precipitation;
e. Characteristics of the cover, including material, final
surface contours, thickness, porosity and permeability, slope, length of run of
slope, and type of vegetation on the cover; and
f. Geological and soil profiles and surface and subsurface
hydrology of the site.
16. Additionally, during the post-closure care period, the
owner or operator of a hazardous waste landfill shall comply with the
requirements of 40 CFR 265.116 and the following items:
a. Maintain the function and integrity of the final cover as
specified in the approved closure plan;
b. Maintain and monitor the leachate collection, removal, and
treatment system, if present, to prevent excess accumulation of the leachate in
the system;
c. Maintain and monitor the landfill gas collection and
control system, if present, to control the vertical and horizontal escape of
gases;
d. Protect and maintain, if present, surveyed benchmarks; and
e. Restrict access to the landfill as appropriate for its
post-closure use.
17. The underground injection of hazardous waste for treatment,
storage or disposal shall be prohibited throughout the Commonwealth of
Virginia.
18. Regulated units of the facility are those units used for
storage treatment or disposal of hazardous waste in surface impoundments, waste
piles, land treatment units, or landfills that received hazardous waste after
July 26, 1982. In addition to the requirements of Subpart G of 40 CFR Part 265, owners or operators of
regulated units who manage hazardous wastes in regulated units shall comply
with the closure and post-closure requirements contained in Subpart G of 40 CFR
Part 264, Subpart H of 40 CFR Part
264, and Subpart K of 40 CFR Part 264 through Subpart N of 40 CFR Part 264, as
applicable, and shall comply with the requirements in Subpart F of 40 CFR Part
264 during any post-closure care period and for the extended ground water
monitoring period, rather than the equivalent requirements contained in 40 CFR
Part 265. The following provisions shall also apply:
a. For owners or operators of surface impoundments or waste
piles included above who intend to remove all hazardous wastes at closure in
accordance with 40 CFR 264.228(a)(1)
or 40 CFR 264.258(a), as applicable, submittal of contingent closure and
contingent post-closure plans is not required. However, if the facility is
subsequently required to close as a landfill in accordance with Subpart N of 40
CFR Part 264, a modified closure plan shall be submitted no more than 30 days
after such determination. These plans will be processed as closure plan
amendments. For such facilities, the corresponding post-closure plan shall be
submitted within 90 days of the determination that the unit shall be closed as
a landfill.
b. A permit application as required under 9VAC20-60-270 to
address the post-closure care requirements of 40 CFR
264.117 and for ground water monitoring requirements of 40 CFR 264.98, 40 CFR
264.99, or 40 CFR 264.100, as
applicable, shall be submitted for all regulated units that fail to satisfy the
requirements of closure by removal or decontamination in 40 CFR 264.228(a)(1), 40 CFR 264.258(a), or 40 CFR 264.280(d) and 40 CFR 264.280(e), as
applicable. The permit application shall be submitted at the same time as the
closure plan for those units closing with wastes in place and six months
following the determination that closure by removal or decontamination is
unachievable for those units attempting such closure. The permit application
shall address the post-closure care maintenance of both the final cover and the
ground water monitoring wells as well as the implementation of the applicable
ground water monitoring program whenever contaminated soils, subsoils, liners,
etc., are left in place. When all contaminated soils, subsoils, liners, etc.,
have been removed yet ground water contamination remains, the permit
application shall address the post-closure care maintenance of the ground water
monitoring wells as well as the implementation of the applicable ground water
monitoring program.
c. In addition to the requirements of 40 CFR
264.112(d)(2)(i) for requesting an extension to the one-year limit, the owner
or operator shall demonstrate that he will continue to take all steps to
prevent threats to human health and the environment.
d. In addition to the requirements of 40 CFR 264.119(c), the
owner or operator shall also request a modification to the post-closure permit
if he wishes to remove contaminated structures and equipment.
19. In 40 CFR 265.71, the terms "EPA" and
"Environmental Protection Agency" shall mean the United States
Environmental Protection Agency, and the reference to "system" means
the United States Environmental Protection Agency's national electronic
manifest system.
20. Regardless of the provisions of 9VAC20-60-18, the
requirements of 40 CFR 265.71(j) are not incorporated into this chapter.
21. Requirements for mercury-containing lamp recycling
facilities. The following requirements apply to all facilities that recover or
reclaim mercury from lamps:
a. All owners and operators of mercury-containing lamp
recycling facilities shall:
(1) Have established markets for the utilization of reclaimed
materials and be able to identify these markets to the department;
(2) Only introduce into the processing equipment lamps or
devices for which the equipment was specifically designed to process and operate
and maintain processing equipment consistent with the equipment manufacturer's
specifications; and
(3) Not speculatively accumulate the materials.
b. If a mercury-containing lamp recycling facility's
processed materials are to be delivered to a facility other than a mercury
reclamation facility, the owner or operator shall:
(1) Demonstrate proper equipment operation and efficiency
by sampling and analytical testing of the processed materials. The testing
shall ensure that such processed materials (i) have less than three parts per
million of "average mercury" during each consecutive 12-week time
period of operations ("average mercury" shall be calculated pursuant
to subdivision 21 b (3) of this subsection); (ii) have less than five parts per
million of total mercury as reported in the "weekly composite sample of
process operations" ("weekly composite sample of process
operations" shall be calculated pursuant to subdivision 21 b (3) of this
subsection); (iii) are not a hazardous waste; and (iv) comply with 40 CFR
Part 268, if applicable.
(2) Retest, reprocess, or deliver to a mercury reclamation
facility processed materials that are in excess of the allowable levels of
mercury specified in subdivision 21 b (1) of this subsection.
(3) Sample and perform analytical testing of the processed
material for total mercury as follows:
(a) Facility operators shall take daily physical samples of
the mercury-containing materials at the point at which they exit the processing
equipment. These samples shall be representative of the materials
processed during that day.
(b) At the beginning of each week, the prior week's daily
samples shall be consolidated into one weekly sample that shall be submitted
for chemical analysis of total mercury content using an approved EPA methodology.
At least three separate daily samples shall be taken in order to obtain a
weekly sample. When a facility is not operating at least three days during a
week, that week will be dropped out of the 12-week rolling average as
calculated under subdivision 21 b (3) (c) of this subsection. However, all
daily samples that are in a week that has been dropped out shall be counted
towards the very next weekly sample that is included in a 12-week rolling
average. The result of this analysis shall be considered the "weekly
composite sample of process operations."
(c) The "average mercury" value calculation shall be
the rolling average of weekly composite sample results from samples taken
during the most recent 12-week time period with each new weekly composite sample
result replacing the oldest sample result that was used in the previous 12-week
period.
c. Mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities shall ensure
that the separated materials that are generated from their operations are
suitable and safe for their intended end use and shall bear the burden of
responsibility for the safety of these materials sold or delivered from the
operations. Facilities shall notify in writing receiving sources, other than
mercury reclamation facilities, of the amount and type of any hazardous
substances present in the processed materials as demonstrated by laboratory
analysis.
d. Operating requirements. Mercury-containing lamp recycling
facilities shall be operated in accordance with the following requirements:
(1) Mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities shall control
mercury emissions through the use of a single air handling system with
redundant mercury controls and comply with the following:
(a) The owner or operator shall operate, monitor, and maintain
an air handling system with redundant air pollution control equipment in order
to reduce the mercury content of the air collected during the volume reduction
and mercury recovery and reclamation processes.
(b) Redundant air pollution control equipment shall
incorporate at least two carbon filters or equivalent technology arranged in a
series so that the air passes through both filters before being released. In
the event of a single filter failure, each filter shall be designed to ensure
compliance with the risk-based protectiveness standards for mercury vapor
provided in subdivision 21 e of this subsection.
(c) A sample of air shall be collected after the first carbon
filter (or equivalent technology) and upstream of the second once each
operating day while mercury-containing lamps or devices are being processed.
The mercury content of the sample shall be determined for comparison with the
risk-based protectiveness standards provided in subdivision 21 e of this
subsection.
(d) The owner or operator shall operate, monitor, and maintain
the air pollution control equipment in such a manner as not to exceed the
risk-based protectiveness standards under subdivision 21 e of this subsection
for mercury vapor downstream of the first carbon filter (or equivalent
technology) and upstream of the second carbon filter.
(2) The area in which the processing equipment is located
shall be fully enclosed and kept under negative pressure while processing
mercury-containing lamps or devices.
e. Testing for mercury releases from lamp crushing units shall
be performed using a mercury vapor analyzer that has been approved for the
application by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration or the
Virginia Department of Labor and Industry or a comparable device that has been
calibrated by the manufacturer or laboratory providing the equipment. Mercury
vapor monitors used for testing must be capable of detecting mercury at the
applicable concentrations provided below or lower in air and must be equipped
with a data recording device to provide a record of measurements taken. Mercury
monitoring data shall be documented and available for inspection in accordance
with subdivision 21 g of this subsection. The acute exposure protectiveness
standard is 300 µg/m3 for a 10-minute exposure with the understanding
that the acute exposure protectiveness standard is considered a ceiling value
and at no time during bulb crushing operation will the air concentrations of
mercury exceed 300 µg/m3. The following are risk-based
protectiveness standards at a distance of five feet from the bulb crushing
unit:
|
Monthly Bulb Crushing Duration
(X Hours/Month)*
|
Chronic Exposure Air Emission
Limit (µg/m3)
|
Acute Exposure Air Emission
Limit (µg/m3)
|
|
X = 32
|
1.314skin µg/m3
|
300 µg/m3
|
|
8 < X < 32
|
6.317 skin µg/m3
|
300 µg /m3
|
|
X = 8
|
27.375 skin µg/m3
|
300 µg/m3
|
|
*Monthly crushing duration is determined based on the
maximum number of hours that bulb crushing occurred in any one month over the
last 12-month period.
|
f. Closure. Mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities must
prepare and maintain a closure plan conforming to the requirements of 40 CFR
Part 265, Subpart G as adopted by reference in this section. Financial
assurance shall be provided to the department in accordance with 40 CFR Part
265, Subpart H as adopted by reference in this section.
g. Recordkeeping requirements. The owner or operator of a
mercury-containing lamp recycling facility shall maintain records of monitoring
information that (i) specify the date, place, and time of measurement; (ii)
provide the methodology used; and (iii) list the analytical results. The
records maintained shall include all calibration and maintenance records of
monitoring equipment. The owner or operator shall retain records of all
monitoring data and supporting information available for department inspection
for a period of at least three years from the date of collection.
22. In 40 CFR 265.12, the term "EPA" shall mean
the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
9VAC20-60-268. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 268 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 268 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials and other ancillaries that are a part of 40 CFR Part 268 are also
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
268 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. In 40 CFR 268.1(e)(3), the term "EPA" means the
United States Environmental Protection Agency.
2. In 40 CFR 268.1(f) and wherever elsewhere in Title 40 of
the Code of Federal Regulations there is a listing of universal wastes or a
listing of hazardous wastes that are the subject of provisions set out in 40
CFR Part 273 as universal wastes, it shall be amended by addition of the
following sentence: "In addition to the hazardous wastes listed herein,
the term "universal waste" and all lists of universal waste or waste
subject to provisions of 40 CFR Part 273 shall include those hazardous wastes
listed in Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et seq.) of the Virginia Hazardous Waste
Management Regulations as universal wastes, under such terms and requirements
as shall therein be ascribed."
3. In 40 CFR 268.5, 40 CFR 268.6, 40 CFR 268.10, 40 CFR
268.11, 40 CFR 268.12, 40 CFR 268.40(b), 40 CFR 268.42(b),
and 40 CFR 268.44(a) through (g) (m), the term
"Administrator" shall mean the administrator Administrator
of the United States Environmental Protection Agency or his designee, the term
"Regional Administrator" shall mean the regional administrator
Regional Administrator of the United States Environmental Protection
Agency for Region III or his designee, and the term "EPA" shall mean
the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
4. In 40 CFR 268.9(d) 268.7(d), the term
"EPA Region or authorized State" shall mean the Commonwealth of
Virginia.
5. 40 CFR 268.13 is not included in the incorporation of 40 CFR
Part 268 by reference and is not a part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste
Management Regulations.
6. Any applications or petitions made to the director or the
department in compliance with 40 CFR 268.44 shall comply with procedures
of Part XIV (9VAC20-60-1370 et seq.) of these regulations.
7. In Subpart C of 40 CFR Part 268 there are dates on which a
provision is or was to begin and dates on which national capacity variances
expires or expired. None of these dates prior to the effective date of these
regulations shall be incorporated by reference or be a part of the Virginia
Hazardous Waste Management Regulations. Requirements associated with these
expired dates shall be considered to be currently in effect. This exclusion
from these regulations shall not be considered to remove or diminish any
responsibility a person has or had regarding these dates under federal
requirements related to the dates or during the interim following these dates.
9VAC20-60-270. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 270 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, those regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 270 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials and other ancillaries that are a part of incorporated sections of 40 CFR
Part 270 are also hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste
Management Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
270 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. In 40 CFR Part 270 and wherever elsewhere in Title 40 of
the Code of Federal Regulations there is a listing of universal wastes or a
listing of hazardous wastes that are the subject of provisions set out in 40
CFR Part 273 as universal wastes, it shall be amended by addition of the
following sentence: "In addition to the hazardous wastes listed herein,
the term "universal waste" and all lists of universal waste or waste
subject to provisions of 40 CFR Part 273 shall include those hazardous wastes
listed in Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et seq.) of the Virginia Hazardous Waste
Management Regulations as universal wastes, under such terms and requirements
as shall therein be ascribed."
2. In 40 CFR 270.5, the term "Administrator" shall
mean the administrator Administrator of the United States
Environmental Protection Agency or his designee.
3. In 40 CFR 270.5, the term "Regional
Administrator" shall mean the regional administrator Regional
Administrator of Region III of the United States Environmental Protection
Agency or his designee.
4. The underground injection of hazardous waste for treatment,
storage or disposal shall be prohibited throughout the Commonwealth of Virginia,
and no permits shall be issued for underground injection facilities.
5. Validity of the federal HWM permits. This section replaces
40 CFR 270.51, which is not included in the incorporation of 40 CFR Part 270 by
reference and is not a part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
a. Hazardous waste management facilities located in Virginia
which possess an effective final RCRA permit issued by the United States
Environmental Protection Agency will be considered to possess a valid Virginia
hazardous waste management permit for the duration of the unexpired term of the
federal permit, provided that:
(1) The facility remains in compliance with all of the
conditions specified in the federal permit;
(2) The operator submits a complete copy of the federal permit
to the department no later than the effective date of the federal permit; and
(3) The owner and operator of the facility submit a request to
continue the federal permit addressed to the department.
b. Federal permits issued to hazardous waste management
facilities located in Virginia by the United States Environmental Protection
Agency pursuant to HSWA requirements which constitute the federal portion of
the combined Virginia--United States Environmental Protection Agency RCRA permits
are considered, for the purposes of this chapter, as addenda to the Virginia
permits and will remain in effect during the unexpired term of the Virginia
permit.
6. All permit applications and reapplications required by
these regulations shall be accompanied by an appropriate permit application fee
as specified in Part XII (9VAC20-60-1260 et seq.) of this chapter. Applications
or reapplications not accompanied by such fees will not be considered complete.
The director shall not issue a permit before receiving a complete application
except permits by rule, emergency permits, or continued federal permits. In
addition, an application for a permit is not complete until the department
receives an application form and any supplemental information, which are completed
to the department's satisfaction. The completeness of any application for a
permit shall be judged independently of the status of any other permit
application or permit for the same facility or activity. In cases where Part A
of the application was first submitted to the United States Environmental
Protection Agency Administrator, a copy of such submission shall also be sent
to the department.
7. Interim status.
a. The director may deny interim status to any owner or
operator if, at the time the Part A application is submitted, the facility is
in violation of any regulation of the board so as to pose a substantial present
or potential hazard to human health or environment.
b. Unless subject of an exception specified in 40 CFR 270.73, interim status terminates when
final disposition of a permit application is made or when interim status is
terminated by the director. Interim status may be terminated for any of the
following reasons:
(1) Failure to submit a completed Part B application on time;
(2) Failure to furnish any information required by this
chapter;
(3) Falsification, misrepresentation or failure to fully
disclose any information submitted or required to be kept under this chapter;
(4) Violation of this chapter; and
(5) A determination that the facility poses a significant
threat to public health or the environment.
c. The director may terminate the interim status upon
receiving a voluntary request for such an action from the owner and the
operator of the facility.
(1) To be considered for voluntary termination such request
shall:
(a) Be received by the department prior to the issuance of the
request to submit Part B of the permit application in accordance with this
section; and
(b) Be accompanied by a waiver of procedures contained in this
section.
(2) Termination under this part will not be granted to the
owner and operator of the facility:
(a) Which is not in compliance with the standards contained in
9VAC20-60-265; or
(b) When termination proceedings have been instituted under
this section.
d. The effective date of the termination of the interim status
will be determined by the director to allow for proper closure of the facility
in accordance with Subpart G of 40 CFR Part 264 and Subpart G of 40 CFR Part
265, as applicable.
8. Each permit shall include permit conditions necessary to
achieve compliance with the Virginia Waste Management Act (§ 10.1-1400 et seq.
of the Code of Virginia) and regulations, including each of the applicable
requirements specified in this part (Part III) of these regulations. In
satisfying this provision, the director may incorporate applicable requirements
of Part III directly into the permit or establish other permit conditions that
are based on these requirements.
9. In addition to the other general information requirements
to be part of the contents of any Part B in 40 CFR 270.14(b), the following
information is required for all hazardous waste management facilities, except
as provided otherwise:
a. A copy of the general inspection schedule required by 40
CFR 264.15(b). Include, where applicable, as part of the inspection schedule,
specific requirements in 40 CFR 264.174, 40 CFR 264.193(i), 40 CFR
264.195, 40 CFR 264.226, 40 CFR
264.254, 40 CFR 264.273, 40 CFR
264.303, 40 CFR 264.573, 40 CFR 264.574, 40 CFR
264.602, 40 CFR 264.1033, 40 CFR 264.1052, 40 CFR
264.1053, and 40 CFR 264.1058.
b. Traffic pattern, estimated volume (number, types of
vehicles) and control; describe access road surfacing and load bearing
capacity; show traffic control signals.
10. A period of 30 days shall elapse between the date of
public notice and the date of a public hearing under 40 CFR 270.42(b)(4)
and 40 CFR 270.42(c)(4).
11. Notices given under 40 CFR 270.30(l)(1) shall be written.
12. The following additional information is required from
owners or operators of facilities that store or treat hazardous waste in waste
piles if an exemption is sought to Subpart F of 40 CFR Part 264 and 40 CFR
264.251 as provided in 40 CFR 264.250(c) and 40 CFR 264.90(b)(2):
a. An explanation of how the standards of 40 CFR 264.250(c)
will be complied with; and
b. Detailed plans and an engineering report describing how
the requirements of 40 CFR 264.90(b)(2) will be met Reserved.
13. The agencies of the Commonwealth publish notices of regulatory
activity, permit hearings and other official notices in the Virginia Register.
Any references in incorporated federal text that indicate a publication is to
be made in the Federal Register shall be construed to mean the Virginia
Register when such publication is to be made by an agency of the Commonwealth.
14. Appeal rights and procedures related to a remedial action
plan (RAP) included in 40 CFR 270.155, especially appeals to the EPA
Environmental Appeals Board, are not incorporated into these regulations.
Appeals of actions related to the content or process of developing a RAP will
be governed by the Administrative Process Act, Chapter 40 (§ 2.2-4000 et
seq.) of Title 2.2 of the Code of Virginia.
15. The conditions of an expired permit continue in force
until the effective date of the new permit if the permittee has submitted a
timely reapplication that is a complete application for a new permit;
and the director, through no fault of the permittee, does not issue a new
permit with an effective date on or before the expiration date of the previous
permit. Permits that are continued remain fully effective and enforceable.
When the permittee is not in compliance with the conditions of
the expiring or expired permit, the director may choose to do any or all of the
following:
a. Initiate enforcement action based on the permit that has
been continued;
b. Issue a notice of intent to deny the new permit. If the
permit is denied, the owner or operator would then be required to cease
activities authorized by the continued permit or be subject to enforcement
action for operating without a permit;
c. Issue a new permit with appropriate conditions; or
d. Take other actions authorized by this chapter.
16. Part XII (9VAC20-60-1260 through 9VAC20-60-1285) 9VAC20-60-1286)
of this chapter applies to all permitted facilities, to facilities operating
under interim status, to facilities subject to an order or agreement, and to
all large quantity generators. In addition to permit application fees, a
permitted treatment, storage, and disposal facility is assessed an annual fee.
A facility that operates under interim status, a facility that is subject to an
order or agreement, and a large quantity generator are also assessed annual
fees.
17. Regardless of the provisions of 9VAC20-60-18, the
revisions to 40 CFR Part 270 as promulgated by U.S. EPA on October 30, 2008,
(73 FR 64757-64788) (definition of solid waste rule) are not adopted
herein.
18. In 40 CFR 270.5, the term "Director" and
"State Director" shall mean the Director of the Department of
Environmental Quality or his designee.
9VAC20-60-273. Adoption of 40 CFR Part 273 by reference.
A. Except as otherwise provided, the regulations of the
United States Environmental Protection Agency set forth in 40 CFR Part 273 are
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations. Except as otherwise provided, all material definitions, reference
materials and other ancillaries that are a part of 40 CFR Part 273 are also
hereby incorporated as part of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management
Regulations.
B. In all locations in these regulations where 40 CFR Part
273 is incorporated by reference, the following additions, modifications, and
exceptions shall amend the incorporated text for the purpose of its
incorporation into these regulations:
1. In 40 CFR 273.32(a)(3), the term "EPA" shall mean
the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
2. In addition to universal
wastes included in 40 CFR Part 273, other wastes are defined to be universal wastes
in Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et seq.) of these regulations. Part XVI also
contains waste specific requirements associated with the waste defined to be
universal waste therein. In 40 CFR 273.1, the definitions in 40 CFR 273.9,
and wherever elsewhere in Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations there is
a listing of universal wastes or a listing of hazardous waste that are the
subject of provisions set out in 40 CFR Part 273 as universal wastes, it shall
be amended by addition of the following sentence: "In addition to the
hazardous wastes listed here, the term "universal waste" and all
lists of universal waste or waste subject to provisions of 40 CFR Part 273
shall include those hazardous wastes listed in Part XVI (9VAC20-60-1495 et seq.)
of the Virginia Hazardous Waste Management Regulations as universal wastes, in
accordance with the terms and requirements described." Any listing of
universal wastes in 40 CFR Part 273 shall incorporate the universal wastes set
out in Part XVI in a manner identical to those included in the federal text;
whether, for example, as in 40 CFR 273.32(b)(4), 40 CFR 273.32(b)(5), 40 CFR
273.39(b)(2), and 40 CFR 273.62(a)(20) or as items to be included in a
calculation or requirement as in the definitions of "Large Quantity Handler
of Universal Waste" and "Small Quantity Handler of Universal
Waste."
3. In addition to the requirements contained in 40 CFR
273, the following requirements shall apply:
a. A used lamp shall be considered to be discarded and a waste
on the date the generator permanently removes it from its fixture. An unused
lamp becomes a waste on the date the generator discards it since that is the
date on which he is deemed to have decided to discard it in accordance with 40
CFR 273.5(c)(2).
b. A handler having a waste subject to the requirements of 40
CFR 273.13(a)(3)(i) or 40 CFR 273.33(a)(3)(l) is also subject to 9VAC20-60-270
and Parts IV (9VAC20-60-305 et seq.), VII (9VAC20-60-420 et seq.), and XII
(9VAC20-60-1260 et seq.) of this chapter.
c. Small and large quantity handlers of universal waste (i)
may only crush mercury-containing lamps for size reduction at the site of
generation or under the control of the generator as defined in 9VAC20-60-1505 B
4 and (ii) shall comply with the applicable mercury-containing lamps crushed
for size reduction requirements of 9VAC20-60-1505.
d. All large quantity handlers of universal waste lamps (i.e.,
generators who accumulate 5000 kilograms or more of universal waste lamps) must
prepare and maintain a closure plan conforming to the requirements of 40 CFR
Part 264, Subpart G as adopted by reference in 9VAC20-60-264. Financial
assurance shall be provided to the department in accordance with 40 CFR Part
264, Subpart H as adopted by reference in 9VAC20-60-264.
e. The owner or operator of a destination facility that
recycles mercury-containing lamps with or without storing the
mercury-containing lamps before they are recycled must comply with all
applicable requirements of 9VAC20-60-264 B 34 and 9VAC20-60-265 B 21 for
mercury-containing lamp recycling facilities.
4. In 40 CFR 273 Subpart F the term "EPA" shall
mean the United States Environmental Protection Agency, and the term
"Administrator" shall mean the Administrator of the United States
Environmental Protection Agency or his designee.
5. In 40 CFR 273 Subpart G, the term
"Administrator" shall mean the Administrator of United States
Environmental Protection Agency or his designee.
VA.R. Doc. No. R18-5265; Filed February 12, 2018, 9:27 a.m.
TITLE 12. HEALTH
REGISTRAR'S NOTICE: The following regulatory action is exempt from Article 2 of the Administrative Process Act in accordance with § 2.2-4006 A 4 c of the Code of Virginia, which excludes regulations that are necessary to meet the requirements of federal law or regulations, provided such regulations do not differ materially from those required by federal law or regulation. The State Board of Health will receive, consider, and respond to petitions by any interested person at any time with respect to reconsideration or revision.
Title of Regulation: 12VAC5-481. Virginia Radiation Protection Regulations (amending 12VAC5-481-10, 12VAC5-481-2970, 12VAC5-481-3000, 12VAC5-481-3130).
Statutory Authority: § 32.1-229 of the Code of Virginia.
Effective Date: April 5, 2018.
Agency Contact: Steve Harrison, Director, Office of Radiological Health, Virginia Department of Health, 109 Governor Street, Richmond, VA 23219, telephone (804) 864-8151, FAX (804) 864-8155, or email steve.harrison@vdh.virginia.gov.
Summary:
As an agreement state with the federal Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), Virginia is required to ensure that its regulations are compatible with Title 10, Energy, of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). This regulatory action amends 12VAC5-481 to implement revisions of 10 CFR from 2015. The amendments (i) correct the definition of "written directive," (ii) add Table 3 to the exemption provision in 12VAC5-481-2970 regarding shipment or carriage of certain low-level materials, (iii) change where a licensee must first submit written information prior to using an NRC-approved package, (iv) clarify responsibility for certain quality assurance requirements, and (v) make other technical corrections.
Part I
General Provisions
12VAC5-481-10. Definitions.
The following words and terms as used in this chapter shall have the following meanings unless the context clearly indicates otherwise:
"A1" means the maximum activity of special form radioactive material permitted in a Type A package. This value is listed in Table 1 of 12VAC5-481-3770 F.
"A2" means the maximum activity of radioactive material, other than special form radioactive material, LSA, and SCO material, permitted in a Type A package. This value is listed in Table 1 of 12VAC5-481-3770 F.
"Absorbed dose" means the energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The units of absorbed dose are the gray (Gy) and the rad.
"Absorbed dose rate" means absorbed dose per unit time, for machines with timers, or dose monitor unit per unit time for linear accelerators.
"Accelerator" means any machine capable of accelerating electrons, protons, deuterons, or other charged particles in a vacuum and of discharging the resultant particulate or other radiation into a medium at energies usually in excess of one MeV. For purposes of this definition, "particle accelerator" is an equivalent term.
"Accelerator-produced material" means any material made radioactive by a particle accelerator.
"Access control" means a system for allowing only approved individuals to have unescorted access to the security zone and for ensuring that all other individuals are subject to escorted access.
"Accessible surface" means the external surface of the enclosure or housing of the radiation producing machine as provided by the manufacturer. It also means surface of equipment or of an equipment part that can be easily or accidentally touched by persons without the use of a tool.
"Act" means §§ 32.1-227 through 32.1-238 of the Code of Virginia.
"Active maintenance" means any significant activity needed during the period of institutional control to maintain a reasonable assurance that the performance objectives in 12VAC5-481-2490 and 12VAC5-481-2500 are met. Such active maintenance includes ongoing activities such as the pumping and treatment of water from a disposal unit or one-time measures such as replacement of a disposal unit cover. Active maintenance does not include custodial activities such as repair of fencing, repair or replacement of monitoring equipment, revegetation, minor additions to soil cover, minor repair of disposal unit covers, and general disposal site upkeep such as mowing grass.
"Activity" means the rate of disintegration or transformation or decay of radioactive material. The units of activity are the becquerel (Bq) and the curie (Ci).
"Acute" means a single radiation dose or chemical exposure event or multiple radiation dose or chemical exposure events occurring within a short time (24 hours or less).
"Address of use" means the building or buildings that are identified on the license and where radioactive material may be produced, prepared, received, used, or stored.
"Adult" means an individual 18 or more years of age.
"Agency" means the Radiological Health Program of the Virginia Department of Health.
"Aggregated" means accessible by the breach of a single physical barrier that would allow access to radioactive material in any form, including any devices that contain the radioactive material, when the total activity equals or exceeds a Category 2 quantity of radioactive material as listed in 12VAC5-481-451.
"Agreement state" means any state with which the NRC or the Atomic Energy Commission has entered into an effective agreement under subsection 274b of the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, as amended (42 USC § 2021(b)).
"Airborne radioactive material" means any radioactive material dispersed in the air in the form of dusts, fumes, particulates, mists, vapors, or gases.
"Airborne radioactivity area" means a room, enclosure, or area in which airborne radioactive materials composed wholly or partly of licensed material exist in concentrations:
1. In excess of the derived air concentrations (DACs) specified in Appendix B to 10 CFR Part 20; or
2. To such a degree that an individual present in the area without respiratory protective equipment could exceed, during the hours an individual is present in a week, an intake of 0.6% of the annual limit on intake (ALI) or 12 DAC hours.
"Air kerma" or "K" means kerma in air (see definition of "kerma").
"Air kerma rate" or "AKR" means the air kerma per unit time.
"Air-purifying respirator" means a respirator with an air-purifying filter, cartridge, or canister that removes specific air contaminants by passing ambient air through the air-purifying element.
"Alert" means events may occur, are in progress, or have occurred that could lead to a release of radioactive material but that the release is not expected to require a response by offsite response organizations to protect persons off site.
"Aluminum equivalent" means the thickness of type 1100 aluminum alloy affording the same attenuation, under specified conditions, as the material in question. The nominal chemical composition of type 100 aluminum is 99.00% minimum aluminum, 0.12% copper.
"Analytical x-ray equipment" means equipment used for x-ray diffraction or fluorescence analysis.
"Analytical x-ray system" means a group of components utilizing x-rays or gamma-rays to determine the elemental composition or to examine the microstructure of materials.
"Annual limit on intake" or "ALI" means the derived limit for the amount of radioactive material taken into the body of an adult worker by inhalation or ingestion in a year. ALI is the smaller value of intake of a given radionuclide in a year by the reference man that would result in a committed effective dose equivalent of 0.05 Sv (5 rem) or a committed dose equivalent of 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to any individual organ or tissue. ALI values for intake by ingestion and by inhalation of selected radionuclides are given in Tables 1 and 2 in Appendix B to 10 CFR Part 20.
"Annual refresher safety training" means a review conducted or provided by the licensee or registrant for its employees on radiation safety aspects of industrial radiography. The review shall include, as a minimum, any results of internal inspections, new procedures or equipment, new or revised regulations, and accidents or errors that have been observed. The review shall also provide opportunities for employees to ask safety questions.
"Annually" means at intervals not to exceed one year.
"ANSI" means the American National Standards Institute.
"Approved individual" means an individual whom the licensee has determined to be trustworthy and reliable for unescorted access in accordance with 12VAC5-481-451 and has completed the training required in 12VAC5-481-451.
"Area of use" means a portion of a physical structure that has been set aside for the purpose of producing, preparing, receiving, using, or storing radioactive material.
"Articulated joint" means a joint between two separate sections of a tabletop that provides the capacity for one of the sections to pivot on the line segment along which the sections join.
"As low as is reasonably achievable" or "ALARA" means making every reasonable effort to maintain exposures to radiation as far below the dose limits in these regulations as is practical, consistent with the purpose for which the licensed or registered activity is undertaken, taking into account the state of technology, the economics of improvements in relation to state of technology, the economics of improvements in relation to benefits to the public health and safety, and other societal and socioeconomic considerations, and in relation to utilization of nuclear energy and licensed or registered sources of radiation in the public interest.
"Assembler" means any person engaged in the business of assembling, replacing, or installing one or more components into an x-ray system or subsystem. The term includes the owner of an x-ray system or his employee or agent who assembles components into an x-ray system that is subsequently used to provide professional or commercial services.
"Assigned protection factor" or "APF" means the expected workplace level of respiratory protection that would be provided by a properly functioning respirator or a class of respirators to properly fitted and trained users. Operationally, the inhaled concentration can be estimated by dividing the ambient airborne concentration by the APF.
"Associated equipment" means equipment that is used in conjunction with a radiographic exposure device to make radiographic exposures that drive, guide, or come in contact with the source.
"Atmosphere-supplying respirator" means a respirator that supplies the respirator user with breathing air from a source independent of the ambient atmosphere, and includes supplied-air respirators (SARs) and self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) units.
"Attenuation block" means a block or stack, having dimensions 20 centimeters by 20 centimeters by 3.8 centimeters, of type 1100 aluminum alloy or other materials having equivalent attenuation. The nominal chemical composition of type 100 aluminum is 99.00% minimum aluminum, 0.12% copper.
"Authorized medical physicist" means an individual who:
1. Meets the requirements in 12VAC5-481-1760 and 12VAC5-481-1790; or
2. Is identified as an authorized medical physicist or teletherapy physicist on:
a. A specific medical use license issued by the NRC or another agreement state;
b. A medical use permit issued by an NRC master material licensee;
c. A permit issued by an NRC or another agreement state broad scope medical use licensee; or
d. A permit issued by an NRC master material license broad scope medical use permittee.
"Authorized nuclear pharmacist" means a pharmacist who:
1. Meets the requirements in 12VAC5-481-1770 and 12VAC5-481-1790;
2. Is identified as an authorized nuclear pharmacist on:
a. A specific license issued by the NRC or another agreement state that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy;
b. A permit issued by an NRC master material licensee that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy;
c. A permit issued by an NRC or another agreement state broad scope medical use licensee that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy; or
d. A permit issued by an NRC master material license broad scope medical use permittee that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy;
3. Is identified as an authorized nuclear pharmacist by a commercial nuclear pharmacy that has been authorized to identify authorized nuclear pharmacists; or
4. Is designated as an authorized nuclear pharmacist in accordance with 12VAC5-481-440 I 2.
"Authorized user" means a practitioner of the healing arts who:
1. Meets the requirements in 12VAC5-481-1790 and any of the following:
a. 12VAC5-481-1910;
b. 12VAC5-481-1940;
c. 12VAC5-481-1980;
d. 12VAC5-481-1990;
e. 12VAC5-481-2000;
f. 12VAC5-481-2018;
g. 12VAC5-481-2030;
h. 12VAC5-481-2040 A; or
2. Is identified as an authorized user on:
a. A specific license issued by the NRC or another agreement state that authorizes medical use;
b. A permit issued by an NRC master material licensee that authorizes medical use;
c. A permit issued by an NRC or another agreement state broad scope medical use licensee that authorizes medical use; or
d. A permit issued by an NRC master material license broad scope medical use permittee that authorizes medical use.
"Automatic exposure control" or "AEC" means a device that automatically controls one or more technique factors in order to obtain, at a preselected location, a required quantity of radiation (includes devices such as phototimers and ion chambers).
"Background investigation" means the investigation conducted by a licensee or applicant to support the determination of trustworthiness and reliability.
"Background radiation" means radiation from cosmic sources, naturally occurring radioactive materials, that have not been technologically enhanced, including radon, except as a decay product of source or special nuclear material, and including global fallout as it exists in the environment from the testing of nuclear explosive devices, or from past nuclear accidents such as Chernobyl that contribute to background radiation and are not under the control of the licensee or registrant. "Background radiation" does not include sources of radiation from radioactive materials regulated by the agency.
"Barrier" (See "Protective barrier").
"Beam axis" means a line from the source through the centers of the x-ray fields.
"Beam-limiting device" means a device that provides a means to restrict the dimensions of the x-ray field or useful beam.
"Beam monitoring system" means a system designed and installed in the radiation head to detect and measure the radiation present in the useful beam.
"Beam scattering foil" means a thin piece of material (usually metallic) placed in the beam to scatter a beam of electrons in order to provide a more uniform electron distribution in the useful beam.
"Becquerel" or "Bq" means the SI unit of activity. One becquerel is equal to one disintegration or transformation per second (dps or tps).
"Beneficial attribute" means, as used in Part XVI (12VAC5-481-3460 et seq.) of this chapter, the radioactivity of the product necessary to the use of the product.
"Beneficial to the product" (See "Beneficial attribute").
"Bent beam linear accelerator" means a linear accelerator geometry in which the accelerated electron beam must change direction by passing through a bending magnet.
"Bioassay" means the determination of kinds, quantities or concentrations, and, in some cases, the locations of radioactive material in the human body, whether by direct measurement, in-vivo counting, or by analysis and evaluation of materials excreted or removed from the human body. For purposes of these regulations, "radiobioassay" is an equivalent term.
"Board" means the State Board of Health.
"Brachytherapy" means a method of radiation therapy in which sealed sources are utilized to deliver a radiation dose at a distance of up to a few centimeters, by surface, intracavitary, or interstitial application.
"Buffer zone" means a portion of the disposal site that is controlled by the licensee and that lies under the disposal units and between the disposal units and the boundary of the site.
"Byproduct material" means:
1. Any radioactive material (except special nuclear material) yielded in, or made radioactive by, exposure to the radiation incident to the process of producing or using special nuclear material;
2. The tailings or wastes produced by the extraction or concentration of uranium or thorium from ore processed primarily for its source material content, including discrete surface wastes resulting from uranium solution extraction processes. Underground ore bodies depleted by these solution extraction operations do not constitute "byproduct material" within this definition;
3. a. Any discrete source of radium-226 that is produced, extracted, or converted after extraction, before, on, or after August 8, 2005, for use for a commercial, medical, or research activity; or
b. Any material that:
(1) Has been made radioactive by use of a particle accelerator; and
(2) Is produced, extracted, or converted after extraction, before, on, or after August 8, 2005, for use for a commercial, medical, or research activity; and
4. Any discrete source of naturally occurring radioactive material, other than source material, that:
a. The NRC, in consultation with the Administrator of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, the U.S. Secretary of Energy, the U.S. Secretary of Homeland Security, and the head of any other appropriate federal agency, determines would pose a threat similar to the threat posed by a discrete source of radium-226 to the public health and safety or the common defense and security; and
b. Before, on, or after August 8, 2005, is extracted or converted after extraction for use in a commercial, medical, or research activity.
"C-arm fluoroscope" means an x-ray system in which the image receptor and x-ray tube housing assembly are connected by a common mechanical support system in order to maintain a desired spatial relationship. This system is designed to allow a change in the projection of the beam through the patient without a change in the position of the patient.
"Cabinet radiography" means industrial radiography conducted in an enclosure or cabinet so shielded that every location on the exterior meets the dose limits for individual members of the public as specified in 12VAC5-481-720.
"Cabinet x-ray system" means an x-ray system with the x-ray tube installed in an enclosure independent of existing architectural structures except the floor on which it may be placed. The cabinet x-ray system is intended to contain at least that portion of a material being irradiated, provide radiation attenuation, and exclude personnel from its interior during generation of radiation. Included are all x-ray systems designed primarily for the inspection of carry-on baggage at airline, railroad, and bus terminals, and in similar facilities. An x-ray tube used within a shielded part of a building, or x-ray equipment that may temporarily or occasionally incorporate portable shielding, is not considered a cabinet x-ray system.
"Calendar quarter" means not less than 12 consecutive weeks nor more than 14 consecutive weeks. The first calendar quarter of each year shall begin in January and subsequent calendar quarters shall be so arranged such that no day is included in more than one calendar quarter and no day in any one year is omitted from inclusion within a calendar quarter. The method observed by the licensee or registrant for determining calendar quarters shall only be changed at the beginning of a year.
"Calibration" means the determination of (i) the response or reading of an instrument relative to a series of known radiation values over the range of the instrument or (ii) the strength of a source of radiation relative to a standard.
"Camera" (See "Radiographic exposure device").
"Carrier" means a person engaged in the transportation of passengers or property by land or water as a common, contract, or private carrier, or by civil aircraft.
"Cassette holder" means a device, other than a spot-film device, that supports or fixes the position of an x-ray film (imaging) cassette during an x-ray exposure.
"Category 1 quantities of radioactive material" or "Category 1" means a quantity of radioactive material meeting or exceeding the Category 1 threshold in Table 1 of 12VAC5-481-451. This is determined by calculating the ratio of the total activity of each radionuclide to the Category 1 threshold for that radionuclide and adding the ratios together. If the sum is equal to or exceeds 1, the quantity would be considered a Category 1 quantity. Category 1 quantities of radioactive material do not include the radioactive material contained in any fuel assembly, subassembly, fuel rod, or fuel pellet.
"Category 2 quantities of radioactive material" or "Category 2" means a quantity of radioactive material meeting or exceeding the Category 2 threshold but less than the Category 1 threshold in Table 1 of 12VAC5-481-451. This is determined by calculating the ratio of the total activity of each radionuclide to the Category 2 threshold for that radionuclide and adding the ratios together. If the sum is equal to or exceeds 1, the quantity would be considered a Category 2 quantity. Category 2 quantities of radioactive material do not include the radioactive material contained in any fuel assembly, subassembly, fuel rod, or fuel pellet.
"Certifiable cabinet x-ray system" means an existing uncertified x-ray system that has been modified to meet the certification requirements specified in 21 CFR 1020.40.
"Certificate holder" means a person who has been issued a certificate of compliance or other package approval by the NRC.
"Certificate of compliance" or "CoC" means the certificate issued by the NRC that approves the design of a package for the transportation of radioactive material.
"Certified cabinet x-ray system" means an x-ray system that has been certified in accordance with 21 CFR 1010.2 as being manufactured and assembled pursuant to the provisions of 21 CFR 1020.40.
"Certified components" means components of x-ray systems that are subject to regulations promulgated under P.L. 90-602, the Radiation Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968 of the Food and Drug Administration.
"Certifying entity" means an independent certifying organization meeting the agency's requirements for documenting applicant's training in topics set forth in 12VAC5-481-1320 or equivalent state or NRC regulations.
"CFR" means Code of Federal Regulations.
"Chelating agent" means amine polycarboxylic acids, hydroxycarboxylic acids, gluconic acid, and polycarboxylic acids.
"Chemical description" means a description of the principal chemical characteristics of a low-level radioactive waste.
"Class" means a classification scheme for inhaled material according to its rate of clearance from the pulmonary region of the lung. Materials are classified as D, W, or Y, which applies to a range of clearance half-times: for Class D, Days, of less than 10 days; for Class W, Weeks, from 10 to 100 days; and for Class Y, Years, of greater than 100 days. For purposes of these regulations, "lung class" and "inhalation class" are equivalent terms.
"Closed transport vehicle" means a transport vehicle equipped with a securely attached exterior enclosure that during normal transportation restricts the access of unauthorized persons to the cargo space containing the radioactive material. The enclosure may be either temporary or permanent but shall limit access from top, sides, and ends. In the case of packaged materials, it may be of the "see-through" type.
"cm" means centimeters.
"Coefficient of variation or "C" means the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean value of a population of observations. It is estimated using the following equation:
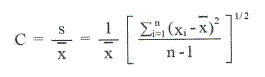
where:
s = Standard deviation of the observed values;
X¯ = Mean value of observations in sample;
xi = ith observation in sample;
n = Number of observations in sample.
"Collective dose" means the sum of the individual doses received in a given period of time by a specified population from exposure to a specified source of radiation.
"Collimator" means a device used to limit the size, shape, and direction of the primary radiation beam. For industrial radiography it means a radiation shield that is placed on the end of the guide tube or directly onto a radiographic exposure device to restrict the size of the radiation beam when the sealed source is cranked into position to make a radiographic exposure.
"Commencement of construction" means taking any action defined as "construction" or any other activity at the site of a facility subject to the regulations in this chapter that has a reasonable nexus to radiological health and safety.
"Committed dose equivalent" or "HT,50" means the dose equivalent to organs or tissues of reference (T) that will be received from an intake of radioactive material by an individual during the 50-year period following the intake.
"Committed effective dose equivalent" or "HE,50" means the sum of the products of the weighting factors (wT) applicable to each of the body organs or tissues that are irradiated and the committed dose equivalent to each of these organs or tissues (HE,50 = S (wT HT,50)).
"Computed tomography" means the production of a tomogram by the acquisition and computer processing of x-ray transmission data.
"Computed tomography dose index" means the integral from -7T to +7T of the dose profile along a line perpendicular to the tomographic plane divided by the product of the nominal tomographic section thickness and the number of tomograms produced in a single scan, that is:
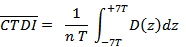
where:
z = Position along a line perpendicular to the tomographic plane;
D(z) = Dose at position z;
T = Nominal tomographic section thickness;
n = Number of tomograms produced in a single scan.
This definition assumes that the dose profile is centered around z = 0 and that, for a multiple tomogram system, the scan increment between adjacent scans is nT.
"Computer-readable medium" means that the regulatory agency's computer can transfer the information from the medium into its memory.
"Consignee" means the designated receiver of the shipment of low-level radioactive waste.
"Consignment" means each shipment of a package or groups of packages or load of radioactive material offered by a shipper for transport.
"Consortium" means an association of medical use licensees and a PET radionuclide production facility in the same geographical area that jointly own or share in the operation and maintenance cost of the PET radionuclide production facility that produces PET radionuclides for use in producing radioactive drugs within the consortium for noncommercial distributions among its associated members for medical use. The PET radionuclide production facility within the consortium must be located at an educational institution or a federal facility or a medical facility.
"Constraint" means each shipment of a package or groups of packages or load of radioactive material offered by a shipper for transport.
"Constraint" or "dose constraint" means a value above which specified licensee actions are required.
"Construction" means the installation of foundations, or in-place assembly, erection, fabrication, or testing for any structure, system, or component of a facility or activity subject to this chapter. The term "construction" does not include:
1. Changes for temporary use of the land for public recreational purposes;
2. Site exploration, including necessary borings to determine foundation conditions or other preconstruction monitoring to establish background information related to the suitability of the site, the environmental impacts of construction or operation, or the protection of environmental values;
3. Preparation of the site for construction of the facility, including clearing of the site, grading, installation of drainage, erosion and other environmental mitigation measures, and construction of temporary roads and borrow areas;
4. Erection of fences and other access control measures that are not related to the safe use of, or security of, radiological materials subject to this chapter;
5. Excavation;
6. Erection of support buildings (e.g., construction equipment storage sheds, warehouse and shop facilities, utilities, concrete mixing plants, docking and unloading facilities, and office buildings) for use in connection with the construction of the facility;
7. Building of service facilities (e.g., paved roads, parking lots, railroad spurs, exterior utility and lighting systems, potable water systems, sanitary sewerage treatment facilities, and transmission lines);
8. Procurement or fabrication of components or portions of the proposed facility occurring at other than the final, in-place location at the facility; or
9. Taking any other action that has no reasonable nexus to radiological health and safety.
"Contact therapy system" means a therapeutic radiation machine with a short target to skin distance (TSD), usually less than five centimeters.
"Contamination" means, as applicable to Part XIII (12VAC5-481-2950 et seq.) of this chapter, the presence of a radioactive substance on a surface in quantities in excess of 0.4 Bq/cm2 (1 x 10-5 µCi/cm2) for beta and gamma emitters and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 0.04 Bq/cm2 (1 x 10-6 µCi/cm2) for all other alpha emitters.
1. Fixed contamination means contamination that cannot be removed from a surface during normal conditions of transport.
2. Nonfixed contamination means contamination that can be removed from a surface during normal conditions of transport.
"Contrast scale" means the change in the linear attenuation coefficient per CTN relative to water, that is:

where:
µx = Linear attenuation coefficient of the material of interest;
µw = Linear attenuation coefficient of water;
 = of the material of interest;
= of the material of interest;
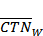 = of water.
= of water.
"Control cable" or "drive" means the cable that is connected to the source assembly and used to drive the source to and from the exposure location.
"Control drive mechanism" means a device that enables the source assembly to be moved into and out of the exposure device.
"Control panel" means that part of the x-ray control upon which are mounted the switches, knobs, pushbuttons, and other hardware necessary for manually setting the technique factors.
"Control tube" means a protective sheath for guiding the control cable. The control tube connects the control drive mechanism to the radiographic exposure device.
"Controlled area" means an area, outside of a restricted area but inside the site boundary, access to which can be limited by the licensee for any reason.
"Conventional simulator" means any x-ray system designed to reproduce the geometric conditions of the radiation therapy equipment.
"Conveyance" means:
1. For transport by public highway or rail any transport vehicle or large freight container;
2. For transport by water any vessel, or any hold, compartment, or defined deck area of a vessel including any transport vehicle on board the vessel; and
3. For transport by any aircraft.
"Cooling curve" means the graphical relationship between heat units stored and cooling time.
"Cradle" means either:
1. A removable device that supports and may restrain a patient above an x-ray table; or
2. A device:
a. Whose patient support structure is interposed between the patient and the image receptor during normal use;
b. Which is equipped with means for patient restraint; and
c. Which is capable of rotation about its long (longitudinal) axis.
"Critical group" means the group of individuals reasonably expected to receive the greatest exposure to residual radioactivity for any applicable set of circumstances.
"Criticality safety index" or "CSI" means the dimensionless number (rounded up to the next tenth) assigned to and placed on the label of a fissile material package, to designate the degree of control of accumulation of packages, overpacks or freight containers containing fissile material during transportation. Determination of the criticality safety index is described in 12VAC5-481-3040, 12VAC5-481-3051, and 10 CFR 71.59. The criticality safety index for an overpack, freight container, consignment, or conveyance containing fissile material packages is the arithmetic sum of the critically safety indices of all the fissile material packages contained within the overpack, freight container, consignment, or conveyance.
"CS" (See "Contrast scale").
"CT" (See "Computed tomography").
"CT conditions of operation" means all selectable parameters governing the operation of a CT x-ray system including, but not limited to, nominal tomographic section thickness, filtration, and the technique factors as defined in these regulations.
"CTDI" (See "Computed tomography dose index").
"CT gantry" means the tube housing assemblies, beam-limiting devices, detectors, and the supporting structures and frames which hold these components.
"CTN" (See "CT number").
"CT number" means the number used to represent the x-ray attenuation associated with each elemental area of the CT image.
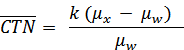
where:
k = A constant, a normal value of 1,000 when the Hounsfield scale of CTN is used;
µx = Linear attenuation coefficient of the material of interest;
µw = Linear attenuation coefficient of water.
"Cumulative air kerma" means the total air kerma accrued from the beginning of an examination or procedure and includes all contribution from fluoroscopic and radiographic irradiation.
"Curie" is a unit of quantity of activity. One curie (Ci) is that quantity of radioactive material that decays at the rate of 3.7E+10 disintegrations or transformations per second (dps or tps).
"Custodial agency" means an agency of the government designated to act on behalf of the government owner of the disposal site.
"Declared pregnant woman" means a woman who has voluntarily informed the licensee, in writing, of her pregnancy and the estimated date of conception. The declaration remains in effect until the declared pregnant woman withdraws the declaration in writing or is no longer pregnant.
"Decommission" means to remove a facility or site safely from service and reduce residual radioactivity to a level that permits release of the property for unrestricted use and termination of the license or release of the property under restricted conditions and termination of the license.
"Decontamination facility" means a facility operating under a commission or agreement state license whose principal purpose is decontamination of equipment or materials to accomplish recycle, reuse, or other waste management objectives, and, for purposes of this chapter, is not considered to be a consignee for LLW shipments.
"Dedicated check source" means a radioactive source that is used to assure the constant operation of a radiation detection or measurement device over several months or years. This source may also be used for other purposes.
"Deep dose equivalent" or "Hd," which applies to external whole body exposure, means the dose equivalent at a tissue depth of one centimeter (1000 mg/cm²).
"Demand respirator" means an atmosphere-supplying respirator that admits breathing air to the facepiece only when a negative pressure is created inside the facepiece by inhalation.
"Department of Energy" means the Department of Energy established by P.L. 95-91, August 4, 1977, 91 Stat. 565, 42 USC § 7101 et seq., to the extent that the Department exercises functions formerly vested in the Atomic Energy Commission, its Chairman, members, officers and components and transferred to the Energy Research and Development Administration and to the Administrator thereof pursuant to §§ 104(b), (c) and (d) of the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974 (P.L. 93-438, October 11, 1974, 88 Stat. 1233 at 1237, 42 USC § 5814, effective January 19, 1975) and retransferred to the U.S. Secretary of Energy pursuant to § 301(a) of the Department of Energy Organization Act (P.L. 95-91, August 4, 1977, 91 Stat. 565 at 577-578, 42 USC § 7151, effective October 1, 1977).
"Depleted uranium" means the source material uranium in which the isotope uranium-235 is less than 0.711 weight percentage of the total uranium present. Depleted uranium does not include special nuclear material.
"Derived air concentration" or "DAC" means the concentration of a given radionuclide in air which, if breathed by the reference man for a working year of 2,000 hours under conditions of light work, results in an intake of one ALI. For purposes of these regulations, the condition of light work is an inhalation rate of 1.2 cubic meters of air per hour for 2,000 hours in a year. DAC values are given in Appendix B to 10 CFR Part 20.
"Derived air concentration-hour" or "DAC hour" means the product of the concentration of radioactive material in air, expressed as a fraction or multiple of the derived air concentration for each radionuclide, and the time of exposure to that radionuclide, in hours. A licensee or registrant may take 2,000 DAC hours to represent one ALI, equivalent to a committed effective dose equivalent of 0.05 Sv (5 rem).
"Detector" (See "Radiation detector").
"Deuterium" means, for the purposes of Part XIII (12VAC5-481-2950 et seq.) of this chapter, deuterium and any deuterium compounds, including heavy water, in which the ratio of deuterium atoms to hydrogen atoms exceeds 1:5000.
"Diagnostic clinical procedures manual" means a collection of written procedures that describes each method (and other instructions and precautions) by which the licensee performs diagnostic clinical procedures, where each diagnostic clinical procedure has been approved by the authorized user and includes the radiopharmaceutical, dosage, and route of administration.
"Diagnostic source assembly" means the tube housing assembly with a beam-limiting device attached.
"Diagnostic x-ray system" means an x-ray system designed for irradiation of any part of the human or animal body for the purpose of diagnosis or visualization.
"Direct scattered radiation" means that scattered radiation that has been deviated in direction only by materials irradiated by the useful beam (See "Scattered radiation").
"Discrete source" means a radionuclide that has been processed so that its concentration within a material has been purposely increased for use for commercial, medical, or research activities.
"Disposable respirator" means a respirator for which maintenance is not intended and that is designed to be discarded after excessive breathing resistance, sorbent exhaustion, physical damage, or end-of-service-life renders it unsuitable for use. Examples of this type of respirator are a disposable half-mask respirator and a disposable escape-only self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA).
"Disposal" means the isolation of wastes from the biosphere inhabited by man and his food chains by emplacement in a land disposal facility.
"Disposal container" means a container principally used to confine low-level radioactive waste during disposal operations at a land disposal facility (also see "high integrity container"). Note that for some shipments, the disposal container may be the transport package.
"Disposal site" means that portion of a land disposal facility that is used for disposal of waste. It consists of disposal units and a buffer zone.
"Disposal unit" means a discrete portion of the disposal site into which waste is placed for disposal. For near-surface disposal, the unit is usually a trench.
"Distinguishable from background" means that the detectable concentration of a radionuclide is statistically different from the background concentration of that radionuclide in the vicinity of the site or, in the case of structures, in similar materials using adequate measurement technology, survey, and statistical techniques.
"Diversion" means the unauthorized movement of radioactive material subject to 12VAC5-481-451 to a location different from the material's authorized destination inside or outside of the site at which the material is used or stored.
"Dose" is a generic term that means absorbed dose, dose equivalent, effective dose equivalent, committed dose equivalent, committed effective dose equivalent, total organ dose equivalent, or total effective dose equivalent. For purposes of these regulations, "radiation dose" is an equivalent term.
"Dose commitment" means the total radiation dose to a part of the body that will result from retention in the body of radioactive material. For purposes of estimating the dose commitment, it is assumed that from the time of intake the period of exposure to retained material will not exceed 50 years.
"Dose equivalent" or "HT" means the product of the absorbed dose in tissue, quality factor, and all other necessary modifying factors at the location of interest. The units of dose equivalent are the sievert (Sv) and rem.
"Dose limits" means the permissible upper bounds of radiation doses established in accordance with these regulations. For purposes of these regulations, "limits" is an equivalent term.
"Dose monitor unit" or "DMU" means a unit response from the beam monitoring system from which the absorbed dose can be calculated.
"Dose profile" means the dose as a function of position along a line.
"Dosimetry processor" means an individual or an organization that processes and evaluates individual monitoring devices in order to determine the radiation dose delivered to the monitoring devices.
"Doubly encapsulated sealed source" means a sealed source in which the radioactive material is sealed within an inner capsule and that capsule is sealed within an outer capsule.
"Drive cable" (See "Control cable").
"Effective dose equivalent" or "HE" means the sum of the products of the dose equivalent (HT) to each organ or tissue and the weighting factor (wT) applicable to each of the body organs or tissues that are irradiated (HE = S wTHT).
"Electronic brachytherapy" means a method of radiation therapy where an electrically generated source of ionizing radiation is placed in or near the tumor or target tissue to deliver therapeutic radiation dosage.
"Electronic brachytherapy device" means the system used to produce and deliver therapeutic radiation including the x-ray tube, the control mechanism, the cooling system, and the power source.
"Electronic brachytherapy source" means the x-ray tube component used in an electronic brachytherapy device.
"Elemental area" means the smallest area within a tomogram for which the x-ray attenuation properties of a body are depicted. (See also "Picture element").
"Embryo/fetus" means the developing human organism from conception until the time of birth.
"Energy compensation source" or "ECS" means a small sealed source, with an activity not exceeding 3.7 MBq (100 µCi), used within a logging tool, or other tool components, to provide a reference standard to maintain the tool's calibration when in use.
"Engineered barrier" means a manmade structure or device that is intended to improve the land disposal facility's ability to meet the performance objectives in these regulations.
"Enriched uranium" (See "Uranium - natural, depleted, enriched").
"Entrance or access point" means any opening through which an individual or extremity of an individual could gain access to radiation areas or to licensed or registered radioactive materials. This includes entry or exit portals of sufficient size to permit human entry, irrespective of their intended use.
"EPA identification number" means the number received by a transporter following application to the Administrator of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency as required by 40 CFR Part 263.
"Equipment" (See "x-ray equipment").
"Escorted access" means accompaniment while in a security zone by an approved individual who maintains continuous direct visual surveillance at all times over an individual who is not approved for unescorted access.
"Exclusive use" means the sole use by a single consignor of a conveyance for which all initial, intermediate, and final loading and unloading are carried out in accordance with the direction of the consignor or consignee. The consignor and the carrier must ensure that any loading or unloading is performed by personnel having radiological training and resources appropriate for safe handling of the consignment. The consignor must issue specific instructions, in writing, for maintenance of exclusive use shipment controls, and include them with the shipping paper information provided to the carrier by the consignor.
"Explosive material" means any chemical compound, mixture, or device that produces a substantial instantaneous release of gas and heat spontaneously or by contact with sparks or flame.
"Exposure" means being exposed to ionizing radiation or to radioactive material.
"Exposure head" means a device that locates the gamma radiography sealed source in the selected working position.
"Exposure rate" means the exposure per unit of time, such as roentgen per minute and milliroentgen per hour.
"External beam radiation therapy" means therapeutic irradiation in which the source of radiation is at a distance from the body.
"External dose" means that portion of the dose equivalent received from any source of radiation outside the body.
"Extremity" means hand, elbow, arm below the elbow, foot, knee, and leg below the knee.
"Facility" means the location, building, vehicle, or complex under one administrative control, at which one or more radiation machines are installed, located or used.
"Fail-safe characteristics" means a design feature that causes beam port shutters to close, or otherwise prevents emergence of the primary beam, upon the failure of a safety or warning device.
"Field emission equipment" means equipment that uses an x-ray tube in which electron emission from the cathode is due solely to the action of an electric field.
"Field-flattening filter" means a filter used to homogenize the absorbed dose rate over the radiation field.
"Field station" means a facility where radioactive sources may be stored or used and from which equipment is dispatched to temporary jobsites.
"Filter" means material placed in the useful beam to preferentially absorb selected radiations. It also means material placed in the useful beam to change beam quality in therapeutic radiation machines subject to Part XV (12VAC5-481-3380 et seq.) of this chapter.
"Filtering facepiece" or "dusk mask" means a negative pressure particulate respirator with a filter as an integral part of the facepiece or with the entire facepiece composed of the filtering medium, not equipped with elastomeric sealing surfaces and adjustable straps.
"Fingerprint orders" means the requirements of 12VAC5-481-451 B or orders issued by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission or the legally binding requirements issued by agreement states that require fingerprints and criminal history records checks for individuals with unescorted access to Category 1 and Category 2 quantities of radioactive material or safeguards information-modified handling.
"Fissile material" means the radionuclides uranium-233, uranium-235, plutonium-239, and plutonium-241, or any combination of these radionuclides. "Fissile material" means the fissile nuclides themselves, not material containing fissile nuclides. Unirradiated natural uranium and depleted uranium and natural uranium or depleted uranium, that has been irradiated in thermal reactors only, are not included in this definition. Certain exclusions from fissile material controls are provided in 10 CFR 71.15.
1. Fissile Class I: A package that may be transported in unlimited numbers and in any arrangement, and that requires no nuclear criticality safety controls during transportation. A transport index is not assigned for purposes of nuclear criticality safety but may be required because of external radiation levels.
2. Fissile Class II: A package that may be transported together with other packages in any arrangement but, for criticality control, in numbers that do not exceed an aggregate transport index of 50. These shipments require no other nuclear criticality safety control during transportation. Individual packages may have a transport index not less than 0.1 and not more than 10.
"Fissile material package" means a fissile material packaging together with its fissile material contents.
"Fit factor" means a quantitative estimate of the fit of a particular respirator to a specific individual, and typically estimates the ratio of the concentration of a substance in ambient air to its concentration inside the respirator when worn.
"Fit test" means the use of a protocol to qualitatively or quantitatively evaluate the fit of a respirator on an individual.
"Fluoroscopic imaging assembly" means a subsystem in which x-ray photons produce a set of fluoroscopic images or radiographic images recorded from the fluoroscopic image receptor. It includes the image receptors, electrical interlocks, if any, and structural material providing linkage between the image receptor and diagnostic source assembly.
"Fluoroscopic irradiation time" means the cumulative duration during an examination or procedure of operator-applied continuous pressure to the device, enabling x-ray tube activation in any fluoroscopic mode of operation.
"Fluoroscopy" means a technique for generating x-ray images and presenting them simultaneously and continuously as visible images. This term has the same meaning as the term "radioscopy" in the standards of the International Electrotechnical Commission.
"Focal spot" or "actual" means the area projected on the anode of the x-ray tube bombarded by the electrons accelerated from the cathode and from which the useful beam originates.
"Former Atomic Energy Commission or NRC licensed facilities" means nuclear reactors, nuclear fuel reprocessing plants, uranium enrichment plants, or critical mass experimental facilities where Atomic Energy Commission or NRC licenses have been terminated.
"Gantry" means that part of a radiation therapy system supporting and allowing movements of the radiation head about a center of rotation.
"Generally applicable environmental radiation standards" means standards issued by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency under the authority of the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, as amended, (42 USC § 2011 et seq.) that impose limits on radiation exposures or levels, or concentrations or quantities of radioactive material, in the general environment outside the boundaries of locations under the control of persons possessing or using radioactive material.
"General environment" means, as used in Part XVI (12VAC5-481-3460 et seq.) of this chapter, the total terrestrial, atmospheric, and aquatic environments outside the site boundary within which any activity, operation, or process authorized by a general or specific license issued under Part XVI, is performed.
"General purpose radiographic x-ray system" means any radiographic x-ray system that, by design, is not limited to radiographic examination of specific anatomical regions.
"Generator" means a licensee who (i) is a waste generator as defined in this chapter, or (ii) is the licensee to whom waste can be attributed within the context of the Low-Level Radioactive Waste Policy Amendments Act of 1985 (42 USC § 2021) (e.g., waste generated as a result of decontamination or recycle activities).
"Gonad shield" means a protective barrier for the testes or ovaries.
"Gray" or "Gy" means the SI unit of absorbed dose. One gray is equal to an absorbed dose of one joule per kilogram (100 rad).
"Guide tube (protection sheath)" means a flexible or rigid tube, or "J" tube, for guiding the source assembly and the attached control cable from the exposure device to the exposure head. The guide tube may also include the connections necessary for attachment to the exposure device and to the exposure head.
"Half-value layer" or "HVL" means the thickness of a specified material that attenuates the beam of radiation to an extent that the AKR is reduced by one-half of its original value. In this definition, the contribution of all scattered radiation, other than any which might be present initially in the beam concerned, is deemed to be excluded.
"Hand-held radiographic unit" means x-ray equipment that is designed to be hand-held during operation.
"Hands-on experience" means experience in all of those areas considered to be directly involved in the radiography process, and includes taking radiographs, calibration of survey instruments, operational and performance testing of survey instruments and devices, film development, posting of radiation areas, transportation of radiography equipment, posting of records and radiation area surveillance, etc., as applicable. Excessive time spent in only one or two of these areas, such as film development or radiation area surveillance, should not be counted toward the 2,000 hours of hands-on experience required for a radiation safety officer in 12VAC5-481-1310 B 2 or the hands-on experience for a radiographer as required by 12VAC5-481-1320 A.
"Hazardous waste" means those wastes designated as hazardous by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulations in 40 CFR Part 261.
"Healing arts" means the art or science or group of arts or sciences dealing with the prevention and cure or alleviation of ailments, diseases or infirmities, and has the same meaning as "medicine" when the latter term is used in its comprehensive sense.
"Healing arts screening" means the testing of human beings using x-ray machines for the detection or evaluation of health indications when such tests are not specifically and individually ordered by a licensed practitioner of the healing arts legally authorized to prescribe such x-ray tests for the purpose of diagnosis or treatment.
"Heat unit" means a unit of energy equal to the product of the peak kilovoltage, milliamperes, and seconds, such as (kVp) times (mA) times (seconds).
"Helmet" means a rigid respiratory inlet covering that also provides head protection against impact and penetration.
"High integrity container" or "HIC" means a container commonly designed to meet the structural stability requirements of 12VAC5-481-2572 and to meet U.S. Department of Transportation requirements for a Type A package.
"High radiation area" means an area, accessible to individuals, in which radiation levels from radiation sources external to the body could result in an individual receiving a dose equivalent in excess of one mSv (0.1 rem) in one hour at 30 centimeters from any source of radiation or 30 centimeters from any surface that the radiation penetrates.
"Hood" means a respiratory inlet covering that completely covers the head and neck and may also cover portions of the shoulders and torso.
"Human use" means the internal or external administration of radiation or radioactive material to human beings.
"Hydrogeologic unit" means any soil or rock unit or zone which by virtue of its porosity or permeability, or lack thereof, has a distinct influence on the storage or movement of groundwater.
"Image intensifier" means a device, installed in its housing, that instantaneously converts an x-ray pattern into a corresponding light image of higher intensity.
"Image receptor" means any device, such as a fluorescent screen, radiographic film, x-ray image intensifier tube, solid-state detector, or gaseous detector that transforms incident x-ray photons either into a visible image or into another form that can be made into a visible image by further transformations. In those cases where means are provided to preselect a portion of the image receptor, the term "image receptor" shall mean the preselected portion of the device.
"Image receptor support device" means, for mammographic systems, that part of the system designed to support the image receptor during mammographic examination and to provide a primary protective barrier.
"Inadvertent intruder" means a person who might occupy the disposal site after closure and engage in normal activities, such as agriculture, dwelling construction, or other pursuits in which an individual might be unknowingly exposed to radiation from the waste.
"Indian tribe" means an Indian or Alaska Native tribe, band, nation, pueblo, village, or community that the U.S. Secretary of the Interior acknowledges to exist as an Indian tribe pursuant to the Federally Recognized Indian Tribe List Act of 1994 (25 USC § 479a).
"Independent certifying organization" means an independent organization that meets the agency's criteria for documenting applicant's training in topics set forth in 12VAC5-481-1320 or equivalent agreement state or NRC regulations.
"Individual" means any human being.
"Individual monitoring" means the assessment of:
1. Dose equivalent (i) by the use of individual monitoring devices or (ii) by the use of survey data; or
2. Committed effective dose equivalent (i) by bioassay or (ii) by determination of the time-weighted air concentrations to which an individual has been exposed, that is, DAC hours. (See the definition of DAC).
"Individual monitoring devices" means devices designed to be worn by a single individual for the assessment of dose equivalent. For purposes of these regulations, "personnel dosimeter" and "dosimeter" are equivalent terms. Examples of individual monitoring devices are film badges, thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs), pocket ionization chambers, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dosimeters and personal air sampling devices.
"Industrial radiography" means an examination of the structure of materials by the nondestructive method of utilizing ionizing radiation to make radiographic images.
"Inhalation class" (See "Class").
"Injection tool" means a device used for controlled subsurface injection of radioactive tracer material.
"Inspection" means an official examination or observation including, but not limited to, tests, surveys, and monitoring to determine compliance with rules, regulations, orders, requirements, and conditions of the agency.
"Institutional controls" means: (i) permanent markers placed at a disposal site, (ii) public records and archives, (iii) government ownership and regulations regarding land or resource use, and (iv) other methods of preserving knowledge about the location, design, and contents of a disposal system.
"Instrument traceability" (for ionizing radiation measurements) means the ability to show that an instrument has been calibrated at specified time intervals using a national standard or a transfer standard. If a transfer standard is used, the calibration must be at a laboratory accredited by a program that requires continuing participation in measurement quality assurance with the National Institute of Standards and Technology or other equivalent national or international program.
"Intensity modulated radiation therapy" or "IMRT" means radiation therapy that uses nonuniform radiation beam intensities that have been determined by various computer-based optimization techniques.
"Interlock" means a device arranged or connected such that the occurrence of an event or condition is required before a second event or condition can occur or continue to occur.
"Internal dose" means that portion of the dose equivalent received from radioactive material taken into the body.
"Interruption of irradiation" means the stopping of irradiation with the possibility of continuing irradiation without resetting of operating conditions at the control panel.
"Intruder barrier" means a sufficient depth of cover over the waste that inhibits contact with waste and helps to ensure that radiation exposures to an inadvertent intruder will meet the performance objectives set forth in these regulations, or engineered structures that provide equivalent protection to the inadvertent intruder.
"Irradiation" means the exposure of matter to ionizing radiation.
"Irradiator" means a facility that uses radioactive sealed sources for the irradiation of objects or materials and in which radiation dose rates exceeding five grays (500 rads) per hour exist at one meter from the sealed radioactive sources in air or water, as applicable for the irradiator type, but does not include irradiators in which both the sealed source and the area subject to irradiation are contained within a device and are not accessible to personnel.
"Irradiator operator" means an individual who has successfully completed the training and testing described in 12VAC5-481-2830 and is authorized by the terms of the license to operate the irradiator without a supervisor present.
"Irradiator operator supervisor" means an individual who meets the requirements for an irradiator operator and who physically oversees operation of the irradiator by an individual who is currently receiving training and testing described in 12VAC5-481-2830.
"Isocenter" means the center of the smallest sphere through which the beam axis passes when the equipment moves through a full range of rotations about its common center.
"kBq" means kilobecquerel.
"Kerma" or "K" means the quantity defined by the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements. The kerma is the quotient of dEtr by dm, where dEtr is the sum of the initial kinetic energies of all charged particles liberated by uncharged particles in a mass dm of materials; thus K=dEtr/dm, in units of J/kg, where the special name for the units of kerma is gray (Gy). When the materials is air, the quantity is referred to as "air kerma."
"Kilovolt" or "kV" means the energy equal to that acquired by a particle with one electron charge in passing through a potential difference of 1,000 volts in a vacuum. Current convention is to use kV for photons and keV for electrons.
"Kilovolts peak" (See "Peak tube potential").
"kV" means kilovolts.
"kVp" (See "Peak tube potential").
"kWs" means kilowatt second.
"Land disposal facility" means the land, buildings, structures and equipment that are intended to be used for the disposal of wastes into the subsurface of the land. For purposes of this chapter, a "geologic repository" as defined in 10 CFR Part 60 or 10 CFR Part 63 is not considered a land disposal facility.
"Last image hold radiograph" or "LIH" means an image obtained either by retaining one or more fluoroscopic images, which may be temporarily integrated, at the end of a fluoroscopic exposure or by initiating a separate and distinct radiographic exposure automatically and immediately in conjunction with termination of the fluoroscopic exposure.
"Lay-barge radiography" means industrial radiography performed on any water vessel used for laying pipe.
"Lead equivalent" means the thickness of the material in question affording the same attenuation, under specified conditions, as lead.
"Leakage radiation" means radiation emanating from the diagnostic source assembly or the radiation therapy system except for:
1. The useful beam; and
2. Radiation produced when the exposure switch or timer is not activated.
"Leakage technique factors" means the technique factors associated with the diagnostic source assembly that are used in measuring leakage radiation. They are defined as follows:
1. For diagnostic source assemblies intended for capacitor energy storage equipment, the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated number of exposures in an hour for operation at the maximum-rated peak tube potential with the quantity of charge per exposure being 10 millicoulombs, (10 mAs), or the minimum obtainable from the unit, whichever is larger;
2. For diagnostic source assemblies intended for field emission equipment rated for pulsed operation, the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated number of x-ray pulses in an hour for operation at the maximum-rated peak tube potential; or
3. For all other diagnostic source assemblies, the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated continuous tube current for the maximum-rated peak tube potential.
"Lens dose equivalent" or "LDE" applies to the external exposure of the lens of the eye and is taken as the dose equivalent at a tissue depth of 0.3 cm (300 mg/cm2).
"License" means a license issued by the agency in accordance with the regulations adopted by the board.
"Licensed material" means radioactive material received, possessed, used, transferred or disposed of under a general or specific license issued by the agency.
"Licensee" means any person who is licensed by the agency in accordance with these regulations and the Act.
"Light field" means the area illuminated by light, simulating the radiation field.
"Limits" (See "Dose limits").
"Line-voltage regulation" means the difference between the no-load and the load line potentials expressed as a percent of the load line potential as follows:
Percent line-voltage regulation = 100 (Vn-Vl)/Vl
where:
Vn = No-load line potential; and
Vl = Load line potential.
"Lixiscope" means a portable light-intensified imaging device using a sealed source.
"Local components" means part of an analytical x-ray system and include areas that are struck by x-rays such as radiation source housings, port and shutter assemblies, collimators, sample holders, cameras, goniometers, detectors, and shielding, but do not include power supplies, transformers, amplifiers, readout devices, and control panels.
"Local law-enforcement agency" or "LLEA" means a public or private organization that has been approved by a federal, state, or local government to carry firearms and make arrests, and is authorized and has the capability to provide an armed response in the jurisdiction where the licensed Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material is used, stored, or transported.
"Logging assistant" means any individual who, under the personal supervision of a logging supervisor, handles sealed sources or tracers that are not in logging tools or shipping containers or who performs surveys required by Part XIV (12VAC5-481-3140 et seq.) of this chapter.
"Logging supervisor" means the individual who uses licensed material or provides personal supervision in the use of licensed material at a temporary jobsite and who is responsible to the licensee for assuring compliance with the requirements of this chapter and the conditions of the license.
"Logging tool" means a device used subsurface to perform well-logging.
"Loose-fitting facepiece" means a respiratory inlet covering that is designed to form a partial seal with the face.
"Lost or missing licensed material" means licensed (or registered) source of radiation whose location is unknown. This definition includes, but is not limited to, radioactive material that has been shipped but has not reached its planned destination and whose location cannot be readily traced in the transportation system.
"Lot tolerance percent defective" means, expressed in percent defective, the poorest quality in an individual inspection lot that should be accepted.
"Low specific activity material" or "LSA material" means radioactive material with limited specific activity that is nonfissile or is excepted under 12VAC5-481-2970 C, and that satisfies the descriptions and limits set forth below. Shielding materials surrounding the LSA material may not be considered in determining the estimated average specific activity of the package contents. LSA material must be in one of three groups:
1. LSA-I
a. Uranium and thorium ores, concentrates of uranium and thorium ores, and other ores containing naturally occurring radionuclides that are intended to be processed for the use of these radionuclides;
b. Natural uranium, depleted uranium, natural thorium or their compounds or mixtures, provided they are unirradiated and in solid or liquid form;
c. Radioactive material other than fissile material, for which the A2 value is unlimited; or
d. Other radioactive material in which the activity is distributed throughout and the estimated average specific activity does not exceed 30 times the value for exempt material activity concentration determined in accordance with 12VAC5-481-3720.
2. LSA-II
a. Water with tritium concentration up to 0.8 terabecquerel per liter (20.0 Ci/L); or
b. Other radioactive material in which the activity is distributed throughout and the estimated average specific activity does not exceed 1.0 E-04 A2/g for solids and gases, and 1.0 E-05 A2/g for liquids.
3. LSA-III
Solids (e.g., consolidated wastes, activated materials), excluding powders, that satisfy the requirements of 10 CFR 71.77) in which:
a. The radioactive material is distributed throughout a solid or a collection of solid objects, or is essentially uniformly distributed in a solid compact binding agent (e.g., concrete, bitumen, or ceramic);
b. The radioactive material is relatively insoluble, or it is intrinsically contained in a relatively insoluble material, so that, even under loss of packaging, the loss of radioactive material per package by leaching, when placed in water for seven days, would not exceed 0.1 A2; and
c. The estimated average specific activity of the solid, excluding any shielding material, does not exceed 2.0 E-03 A2/g.
"Low toxicity alpha emitters" means natural uranium, depleted uranium, natural thorium; uranium-235, uranium-238, thorium-232, thorium-228 or thorium-230 when contained in ores or physical or chemical concentrates or tailings; or alpha emitters with a half-life of less than 10 days.
"Lung class" (See "Class").
"mA" means milliampere.
"mAs" means milliampere second.
"Major processor" means a user processing, handling, or manufacturing radioactive material exceeding Type A quantities as unsealed sources or material, or exceeding four times Type B quantities as sealed sources, but does not include nuclear medicine programs, universities, industrial radiographers, or small industrial programs. Type A and B quantities are defined in this section.
"Management" means the chief executive officer or that individual's designee.
"MBq" means megabecquerels.
"Medical event" means an event that meets the criteria in 12VAC5-481-2080.
"Medical institution" means an organization in which several medical disciplines are practiced.
"Medical use" means the intentional internal or external administration of radioactive material or the radiation from radioactive material to patients or human research subjects under the supervision of an authorized user.
"Megavolt" or "MV" means the energy equal to that acquired by a particle with one electron charge in passing through a potential difference of one million volts in a vacuum. (Note: current convention is to use MV for photons and MeV for electrons.)
"Member of the public" means an individual except when that individual is receiving an occupational dose.
"Mineral logging" means any logging performed for the purpose of mineral exploration other than oil or gas.
"Minor" means an individual less than 18 years of age.
"Misadministration" means either:
1. An x-ray teletherapy radiation dose:
a. Involving the wrong patient;
b. Involving the wrong mode of treatment;
c. Involving the wrong treatment site;
d. Where the calculated total administered dose differs from the total prescribed dose by more than 10% when the treatment consists of three or fewer fractions;
e. Where the calculated weekly administered dose differs from the weekly prescribed dose by 30%; or
f. Where the calculated total administered dose differs from the total prescribed dose by more than 20%; or
2. An x-ray brachytherapy radiation dose:
a. Involving the wrong patient;
b. Involving the wrong treatment site; or
c. Where the calculated administered dose differs from the prescribed dose by more than 20%.
"mm" means millimeters.
"Mobile device" means a piece of equipment containing licensed radioactive materials that is either mounted on wheels or casters, or otherwise equipped for moving without a need for disassembly or dismounting, or designed to be hand carried. Mobile devices do not include stationary equipment installed in a fixed location.
"Mobile electronic brachytherapy service" means transportation of an electronic brachytherapy device to provide electronic brachytherapy at an address that is not the address of record.
"Mobile nuclear medicine service" means the transportation and medical use of radioactive material.
"Mobile x-ray equipment" (See "x-ray equipment").
"Mode of operation" means, for fluoroscopy systems, a distinct method of fluoroscopy or radiography provided by the manufacturer and selected with a set of several technique factors or other control settings uniquely associated with the mode. The set of distinct technique factors and control settings for the mode may be selected by the operation of a single control. Examples of distinct modes of operation include normal fluoroscopy (analog or digital), high-level control fluoroscopy, cineradiography (analog and digital), digital subtraction angiography, electronic radiography using the fluoroscopic image receptor, and photospot recording. In a specific mode of operation, certain system variables affecting kerma, AKR, or image quality, such as image magnification, x-ray field size, pulse rate, pulse duration, number of pulses, source-image receptor distance (SID), or optical aperture, may be adjustable or may vary; their variation per se does not comprise a mode of operation different from the one that has been selected.
"Monitor unit" or "MU" (See "Dose monitor unit").
"Monitoring" means the measurement of radiation, radioactive material concentrations, surface area activities or quantities of radioactive material and the use of the results of these measurements to evaluate potential exposures and doses. For purposes of these regulations, "radiation monitoring" and "radiation protection monitoring" are equivalent terms. For Part XI (12VAC5-481-2330 et seq.) of this chapter, it means observing and making measurements to provide data to evaluate the performance and characteristics of the disposal site.
"Movement control center" means an operation center that is remote from the transport activity and that maintains the position information on the movement of radioactive material, receives reports of attempted attacks or thefts, provides a means for reporting these and other problems to appropriate agencies and can request and coordinate appropriate aid.
"Moving beam radiation therapy" means radiation therapy with any planned displacement of radiation field or patient relative to each other, or with any planned change of absorbed dose distribution. It includes arc, skip, conformal, intensity modulation and rotational therapy.
"Multiple tomogram system" means a computed tomography x-ray system that obtains x-ray transmission data simultaneously during a single scan to produce more than one tomogram.
"NARM" means any naturally occurring or accelerator-produced radioactive material. It does not include byproduct, source, or special nuclear material.
"National Sealed Source and Device Registry" or "SSDR" means the national registry that contains the registration certificates, maintained by the NRC, that summarize the radiation safety information for sealed sources and devices, and describes the licensing and use conditions approved for the product.
"Nationally tracked source" means a sealed source containing a quantity equal to or greater than Category 1 or Category 2 levels of any radioactive material listed in 12VAC5-481-3780. In this context a sealed source is defined as radioactive material that is sealed in a capsule or closely bonded, in a solid form and that is not exempt from regulatory control. It does not mean material encapsulated solely for disposal, or nuclear material contained in any fuel assembly, subassembly, fuel rod, or fuel pellet. Category 1 nationally tracked sources are those containing radioactive material at a quantity equal to or greater than the Category 1 threshold. Category 2 nationally tracked sources are those containing radioactive material at a quantity equal to or greater than the Category 2 threshold but less than the Category 1 threshold.
"Natural radioactivity" means radioactivity of naturally occurring nuclides.
"Natural thorium" means thorium with the naturally occurring distribution of thorium isotopes, which is essentially 100 weight percent thorium-232.
"Natural uranium" (See "Uranium - natural, depleted, enriched").
"Near-surface disposal facility" means a land disposal facility in which waste is disposed of within approximately the upper 30 meters of the earth's surface.
"Negative pressure respirator" or "tight fitting" means a respirator in which the air pressure inside the facepiece is negative during inhalation with respect to the ambient air pressure outside the respirator.
"No-later-than arrival time" means the date and time that the shipping licensee and receiving licensee have established as the time at which an investigation will be initiated if the shipment has not arrived at the receiving facility. The no-later-than arrival times may not be more than six hours after the estimated arrival time for shipments of Category 2 quantities of radioactive material.
"Noise" means the standard deviation of the fluctuations in CTN expressed as a percentage of the attenuation coefficient of water. Its estimate (Sn) is calculated using the following expression:
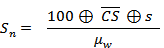
where:
 = Linear attenuation coefficient of the material of interest.
= Linear attenuation coefficient of the material of interest.
µw = Linear attenuation coefficient of water.
s = Standard deviation of the CTN of picture elements in a specified area of the CT image.
"Nominal tomographic section thickness" means the full width at half-maximum of the sensitivity profile taken at the center of the cross-sectional volume over which x-ray transmission data are collected.
"Non-image-intensified fluoroscopy" means fluoroscopy using only a fluorescent screen.
"Nonstochastic effect" means a health effect, the severity of which varies with the dose and for which a threshold is believed to exist. Radiation-induced cataract formation is an example of a nonstochastic effect. For purposes of these regulations, "deterministic effect" is an equivalent term.
"NORM" means any naturally occurring radioactive material. It does not include accelerator produced, byproduct, source, or special nuclear material.
"Normal form radioactive material" means radioactive material that has not been demonstrated to qualify as special form radioactive material.
"Normal operating procedures" mean step-by-step instructions necessary to accomplish the analysis. These procedures shall include sample insertion and manipulation, equipment alignment, routine maintenance by the registrant (or licensee), and data recording procedures, which are related to radiation safety.
"Nominal treatment distance" means:
1. For electron irradiation, the distance from the scattering foil, virtual source, or exit window of the electron beam to the entrance surface of the irradiated object along the central axis of the useful beam.
2. For x-ray irradiation, the virtual source or target to isocenter distance along the central axis of the useful beam. For nonisocentric equipment, this distance shall be that specified by the manufacturer.
"NRC Forms 540, 540A, 541, 541A, 542, and 542A" means official NRC forms referenced in this chapter. Licensees need not use originals of these NRC Forms as long as any substitute forms are equivalent to the original documentation in respect to content, clarity, size, and location of information. Upon agreement between the shipper and consignee, NRC Forms 541 (and 541A) and NRC Forms 542 (and 542A) may be completed, transmitted, and stored in electronic media. The electronic media must have the capability for producing legible, accurate, and complete records in the format of the uniform manifest.
"Nuclear Regulatory Commission" or "NRC" means the NRC or its duly authorized representatives.
"Nuclear waste" means a quantity of source, byproduct or special nuclear material (the definition of nuclear waste in this chapter is used in the same way as in 49 CFR 173.403) required to be in NRC-approved specification packaging while transported to, through or across a state boundary to a disposal site, or to a collection point for transport to a disposal site.
"Occupational dose" means the dose received by an individual in the course of employment in which the individual's assigned duties for the licensee or registrant involve exposure to sources of radiation, whether or not the sources of radiation are in the possession of the licensee, registrant, or other person. Occupational dose does not include doses received from background radiation, from any medical administration the individual has received, from exposure to individuals administered radioactive material and released in accordance with 12VAC5-481-1870, from voluntary participation in medical research programs, or as a member of the public.
"Offshore platform radiography" means industrial radiography conducted from a platform over a body of water.
"Offshore waters" means that area of land and water, beyond the Commonwealth of Virginia's jurisdiction, on or above the U.S. Outer Continental Shelf.
"Open-beam configuration" means an analytical x-ray system in which an individual could accidentally place some part of his body in the primary beam path during normal operation.
"Output" means the exposure rate, dose rate, or a quantity related in a known manner to these rates from a teletherapy unit for a specified set of exposure conditions.
"Package" means the packaging together with its radioactive contents as presented for transport.
1. Fissile material package or Type AF package, Type BF package, Type B(U)F package, or Type B(M)F package means a fissile material packaging together with its fissile material contents.
2. Type A package means a Type A packaging together with its radioactive contents. A Type A package is defined and must comply with the DOT regulations in 49 CFR Part 173.
3. Type B package means a Type B packaging together with its radioactive contents. On approval, a Type B package design is designated by NRC as B(U) unless the package has a maximum normal operating pressure of more than 700 kPa (100 lbs/in2) gauge or a pressure relief device that would allow the release of radioactive material to the environment under the tests specified in 10 CFR 71.73 (hypothetical accident conditions), in which case it will receive a designation B(M). B(U) refers to the need for unilateral approval of international shipments; B(M) refers to the need for multilateral approval of international shipments. There is no distinction made in how packages with these designations may be used in domestic transportation. To determine their distinction for international transportation, see DOT regulations in 49 CFR Part 173. A Type B package approved before September 6, 1983, was designated only as Type B. Limitations on its use are specified in 10 CFR 71.19.
"Packaging" means the assembly of components necessary to ensure compliance with the packaging requirements of these regulations. It may consist of one or more receptacles, absorbent materials, spacing structures, thermal insulation, radiation shielding, and devices for cooling or absorbing mechanical shocks. The vehicle, tie-down system, and auxiliary equipment may be designated as part of the packaging.
"Panoramic dry-source-storage irradiator" means an irradiator in which the irradiations occur in air in areas potentially accessible to personnel and in which the sources are stored in shields made of solid materials. The term includes beam-type dry-source-storage irradiators in which only a narrow beam of radiation is produced for performing irradiations.
"Panoramic irradiator" means an irradiator in which the irradiations are done in air in areas potentially accessible to personnel. The term includes beam-type irradiators.
"Panoramic wet-source-storage irradiator" means an irradiator in which the irradiations occur in air in areas potentially accessible to personnel and in which the sources are stored under water in a storage pool.
"Particle accelerator" (See "Accelerator").
"Patient" means an individual or animal subjected to healing arts examination, diagnosis, or treatment.
"PBL" (See "Positive beam limitation").
"Peak tube potential" means the maximum value of the potential difference across the x-ray tube during an exposure.
"Periodic quality assurance check" means a procedure that is performed to ensure that a previous calibration continues to be valid.
"Permanent radiographic installation" means an enclosed shielded room, cell, or vault, not located at a temporary jobsite, in which radiography is performed.
"Person" means any individual, corporation, partnership, firm, association, trust, estate, public or private institution, group, department of the Commonwealth other than the Department of Health, political subdivision of the Commonwealth, any other state or political subdivision or department thereof, and any legal successor, representative, agent, or department of the foregoing, but not including federal government agencies.
"Personal supervision" means guidance and instruction by the supervisor who is physically present at the jobsite and watching the performance of the operation in such proximity that contact can be maintained and immediate assistance given as required. In radiography it means guidance and instruction provided to a radiographer trainee by a radiographer instructor who is present at the site, in visual contact with the trainee while the trainee is using sources of radiation, and in such proximity that immediate assistance can be given if required.
"Personnel monitoring equipment" (See "Individual monitoring devices").
"Phantom" means a volume of material behaving in a manner similar to tissue with respect to the attenuation and scattering of radiation. This requires that both the atomic number (Z) and the density of the material be similar to that of tissue.
"Physical description" means the items called for on NRC Form 541 to describe a low-level radioactive waste.
"Pool irradiator" means any irradiator at which the sources are stored or used in a pool of water including panoramic wet-source-storage irradiators and underwater irradiators.
"Pharmacist" means an individual licensed by this state to compound and dispense drugs, prescriptions, and poisons.
"Physician" means an individual licensed by this state to prescribe drugs in the practice of medicine.
"Picture element" means an elemental area of a tomogram.
"PID" (See "Position indicating device").
"Pigtail" (See "Source assembly").
"Pill" (See "Sealed source").
"Planned special exposure" means an infrequent exposure to radiation, separate from and in addition to the annual occupational dose limits.
"Portable x-ray equipment" (See "x-ray equipment").
"Position indicating device" means a device on dental x-ray equipment used to indicate the beam position and to establish a definite source-surface (skin) distance. It may or may not incorporate or serve as a beam-limiting device.
"Positive beam limitation" means the automatic or semi-automatic adjustment of an x-ray beam to the size of the selected image receptor, whereby exposures cannot be made without such adjustment.
"Positron emission tomography radionuclide production facility" or "PET" means a facility operating a cyclotron or other particle accelerator for the purpose of producing radionuclides that decay by positron emission.
"Positive pressure respirator" means a respirator in which the pressure inside the respiratory inlet covering exceeds the ambient air pressure outside the respirator.
"Powered air-purifying respirator" or "PAPR" means an air-purifying respirator that uses a blower to force the ambient air through air-purifying elements to the inlet covering.
"Practical examination" means a demonstration through application of the safety rules and principles in industrial radiography including use of all procedures and equipment to be used by radiographic personnel.
"Practical range of electrons" corresponds to classical electron range where the only remaining contribution to dose is from bremsstrahlung x-rays. A further explanation may be found in "Clinical Electron Beam Dosimetry: Report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 25" (Medical Physics 18(1): 73-109, Jan/Feb. 1991) and ICRU Report 35, "Radiation Dosimetry: Electron Beams with Energies Between 1 and 50 MeV", International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements, September 15, 1984.
"Preceptor" means an individual who provides, directs, or verifies training and experience required for an individual to become an authorized user, an authorized medical physicist, an authorized nuclear pharmacist, or a radiation safety officer.
"Prescribed dosage" means the quantity of radiopharmaceutical activity as documented:
1. In a written directive; or
2. Either in the diagnostic clinical procedures manual or in any appropriate record in accordance with the directions of the authorized user for diagnostic procedures.
"Prescribed dose" means:
1. For gamma stereotactic radiosurgery, the total dose as documented in the written directive;
2. For teletherapy, the total dose and dose per fraction as documented in the written directive. The prescribed dose is an estimation from measured data from a specified therapeutic machine using assumptions that are clinically acceptable for that treatment technique and historically consistent with the clinical calculations previously used for patients treated with the same clinical technique; or
3. For brachytherapy, either the total source strength and exposure time, or the total dose, as documented in the written directive.
"Pressure demand respirator" means a positive pressure atmosphere-supplying respirator that admits breathing air to the facepiece when the positive pressure is reduced inside the facepiece by inhalation.
"Primary beam" means radiation that passes through an aperture of the source housing by a direct path from the x-ray tube or a radioactive source located in the radiation source housing.
"Primary dose monitoring system" means a system that will monitor the useful beam during irradiation and that will terminate irradiation when a preselected number of dose monitor units have been delivered.
"Primary protective barrier" means the material, excluding filters, placed in the useful beam to reduce the radiation exposure (beyond the patient and cassette holder) for protection barriers.
"Principal activities," as used in this chapter, means activities authorized by the license that are essential to achieving the purposes for which the license was issued or amended. Storage during which no licensed material is accessed for use or disposal and activities incidental to decontamination or decommissioning are not principal activities.
"Private inspector" means an individual who meets the requirements set forth in 12VAC5-481-340 and who has demonstrated to the satisfaction of the agency that such individual possesses the knowledge, training and experience to measure ionizing radiation, to evaluate safety techniques, and to advise regarding radiation protection needs.
"Product" means, as used in Part XVI (12VAC5-481-3460 et seq.) of this chapter, something produced, made, manufactured, refined, or benefited.
"Product conveyor system" means a system for moving the product to be irradiated to, from, and within the area where irradiation takes place.
"Projection sheath" (See "Guide tube").
"Projector" (See "Radiographic exposure device").
"Protective apron" means an apron made of radiation-attenuating or absorbing materials used to reduce exposure to radiation.
"Protective glove" means a glove made of radiation absorbing materials used to reduce radiation exposure.
"Public dose" means the dose received by a member of the public from exposure to sources of radiation released by the licensee or registrant, or to any other source of radiation under the control of the licensee or registrant. "Public dose" does not include occupational dose, or doses received from background radiation, from any medical administration the individual has received, from exposure to individuals administered radioactive material and released in accordance with 12VAC5-481-1870, or from voluntary participation in medical research programs.
"Pulsed mode" means operation of the x-ray system such that the x-ray tube is pulsed by the x-ray control to produce one or more exposure intervals of duration less than one-half second.
"Pyrophoric material" means any liquid that ignites spontaneously in dry or moist air at or below 130°F (54.4°C) or any solid material, other than one classed as an explosive, which under normal conditions is liable to cause fires through friction, retained heat from manufacturing or processing, or that can be ignited readily and, when ignited, burns so vigorously and persistently as to create a serious transportation, handling, or disposal hazard. Included are spontaneously combustible and water-reactive materials.
"Qualified inspector" means an individual who is granted professional privileges based on education and experience to provide clinical services in diagnostic and therapeutic medical physics.
"Qualified medical physicist" means an individual qualified in accordance with 12VAC5-481-3390 D.
"Qualitative fit test" or "QLFT" means a pass/fail fit test to assess the adequacy of respirator fit that relies on the individual's response to the test agent.
"Quality factor" or "Q" means the modifying factor, that is referenced in 12VAC5-481-240, that is used to derive dose equivalent from absorbed dose.
"Quantitative fit test" or "QNFT" means an assessment of the adequacy of respirator fit by numerically measuring the amount of leakage into the respirator.
"Quarter" means a period of time equal to one-fourth of the year observed by the licensee, approximately 13 consecutive weeks, providing that the beginning of the first quarter in a year coincides with the starting date of the year and that no day is omitted or duplicated in consecutive quarters.
"Rad" means the special unit of absorbed dose. One rad is equal to an absorbed dose of 100 erg per gram or 0.01 joule per kilogram (0.01 gray).
"Radiation" means alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, x-rays, neutrons, high-speed electrons, high-speed protons, and other particles capable of producing ions. For purposes of these regulations, ionizing radiation is an equivalent term. Radiation, as used in these regulations, does not include nonionizing radiation, such as radiowaves or microwaves, visible, infrared, or ultraviolet light.
"Radiation area" means any area, accessible to individuals, in which radiation levels could result in an individual receiving a dose equivalent in excess of 0.05 mSv (0.005 rem) in one hour at 30 centimeters from the source of radiation or from any surface that the radiation penetrates.
"Radiation dose" (See "Dose").
"Radiation field" (See "Useful beam").
"Radiation head" means the structure from which the useful beam emerges.
"Radiation machine" means any device capable of producing radiation except those devices with radioactive material as the only source of radiation.
"Radiation room" means a shielded room in which irradiations take place. Underwater irradiators do not have radiation rooms.
"Radiation safety officer" or "RSO" means an individual who has the knowledge and responsibility to apply appropriate radiation protection regulations and has been assigned such responsibility by the licensee or registrant.
"Radiation safety officer for industrial radiography" means an individual with the responsibility for the overall radiation safety program on behalf of the licensee or registrant and who meets the requirements of 12VAC5-481-1310.
"Radiation safety officer for medical" means an individual who meets the requirements of 12VAC5-481-1750 and 12VAC5-481-1790 or is identified as an RSO on: a medical use license issued by the agency, NRC or another agreement state, or a medical use permit issued by an NRC masters material licensee.
"Radiation therapy physicist" means an individual qualified in accordance with 12VAC5-481-340.
"Radiation therapy simulation system" means a radiographic or fluoroscopic x-ray system intended for localizing the volume to be exposed during radiation therapy and confirming the position and size of the therapeutic irradiation field.
"Radiation therapy system" means a device that delivers radiation to a specific area of the body where cancer cells or tumors are located.
"Radioactive material" means any solid, liquid, or gas which emits radiation spontaneously.
"Radioactive marker" means radioactive material placed subsurface or on a structure intended for subsurface use for the purpose of depth determination or direction orientation.
"Radioactivity" means the transformation of unstable atomic nuclei by the emission of radiation.
"Radiobioassay" (See "Bioassay").
"Radiograph" means an image receptor on which the image is created directly or indirectly by an x-ray pattern and results in a permanent record.
"Radiographer" means any individual who performs or who, in attendance at the site where the sources of radiation are being used, personally supervises industrial radiographic operations and who is responsible to the licensee or registrant for assuring compliance with the requirements of the agency's regulations and the conditions of the license or registration.
"Radiographer certification" means written approval received from a certifying entity stating that an individual has satisfactorily met the radiation safety, testing, and experience criteria in 12VAC5-481-1320.
"Radiographer instructor" means any radiographer who has been authorized by the agency to provide on-the-job training to radiographer trainees in accordance with Part V (12VAC5-481-1170 et seq.) of this chapter.
"Radiographer trainee" means any individual who, under the personal supervision of a radiographer instructor, uses sources of radiation, related handling tools, or radiation survey instruments during the course of his instruction.
"Radiographer's assistant" means any individual who under the direct supervision of a radiographer, uses radiographic exposure devices, sources of radiation, related handling tools, or radiation survey instruments in industrial radiography.
"Radiographic exposure device" means any instrument containing a sealed source fastened or contained therein, in which the sealed source or shielding thereof may be moved, or otherwise changed, from a shielded to unshielded position for purposes of making a radiographic exposure.
"Radiographic operations" means all activities performed with a radiographic exposure device, or with a radiation machine. Activities include using, transporting except by common or contract carriers, or storing at a temporary job site, performing surveys to confirm the adequacy of boundaries, setting up equipment, and any activity inside restricted area boundaries. Transporting a radiation machine is not considered a radiographic operation.
"Radiographic personnel" means any radiographer, radiographer instructor, or radiographer trainee.
"Radiography" means:
1. For radioactive materials: See "Industrial radiography."
2. For x-ray: A technique for generating and recording an x-ray pattern for the purpose of providing the user with an image after termination of the exposure.
"Rating" means the operating limits as specified by the component manufacturer.
"Reasonably maximally exposed individual" means, as used in Part XVI (12VAC5-481-3460 et seq.) of this chapter, a representative of a population who is exposed to TENORM at the maximum TENORM concentration measured in environmental media found at a site along with reasonable maximum case exposure assumptions. The exposure is determined by using maximum values for one or more of the most sensitive parameters affecting exposure, based on cautious but reasonable assumptions, while leaving the others at their mean value.
"Recording" means producing a retrievable form of an image resulting from x-ray photons.
"Redundant beam monitoring system" means a combination of two dose monitoring systems in which each system is designed to terminate irradiation in accordance with a preselected number of dose monitor units.
"Reference man" means a hypothetical aggregation of human physical and physiological characteristics determined by international consensus. These characteristics may be used by researchers and public health employees to standardize results of experiments and to relate biological insult to a common base. A description of the reference man is contained in the International Commission on Radiological Protection report, ICRP Publication 23, "Report of the Task Group on Reference Man."
"Reference plane" means a plane that is displaced from and parallel to the tomographic plane.
"Registrant" means any person who is registered with the agency and is legally obligated to register with the agency pursuant to these regulations and the Act.
"Registration" means registration with the agency in accordance with the regulations adopted by the agency.
"Regulations of the U.S. Department of Transportation" means the regulations in 49 CFR Parts 100 - 189.
"Rem" means the special unit of any of the quantities expressed as dose equivalent. The dose equivalent in rems is equal to the absorbed dose in rad multiplied by the quality factor (1 rem = 0.01 Sv).
"Reportable event" means the administration of either:
1. A diagnostic x-ray exposure where an actual or suspected acute or long-term functional damage to an organ or a physiological system has occurred. Exempt from this reporting requirement is any event when any functional damage to a patient organ or a physiological system that was an expected outcome when the causative procedures were prescribed;
2. A procedure where the patient or operator is injured as a result of a mechanical injury;
3. A teletherapy x-ray or electron dose where the calculated weekly administered dose differs from the weekly prescribed dose by 15% or more; or
4. A brachytherapy x-ray dose where the calculated administered dose differs from the prescribed dose by 10% or more.
"Research and development" means (i) theoretical analysis, exploration, or experimentation; or (ii) the extension of investigative findings and theories of a scientific or technical nature into practical application for experimental and demonstrative purposes, including the experimental production and testing of models, devices, equipment, materials, and processes. Research and development does not include the internal or external administration of radiation or radioactive material to human beings.
"Residential location" means any area where structures in which people lodge or live are located, and the grounds on which such structures are located including, but not limited to, houses, apartments, condominiums, and garages.
"Residual radioactive material" means (i) waste (that the U.S. Secretary of Energy determines to be radioactive) in the form of tailings resulting from the processing of ores for the extraction of uranium and other valuable constituents of the ores and (ii) other waste (that the U.S. Secretary of Energy determines to be radioactive) at a processing site that relates to such processing, including any residual stock of unprocessed ores or low-grade materials. This term is used only with respect to materials at sites subject to remediation under Title I of the Uranium Mill Tailings Radiation Control Act of 1978, as amended.
"Residual radioactivity" means radioactivity in structures, materials, soils, groundwater, and other media at a site resulting from activities under the licensee's control. This includes radioactivity from all licensed and unlicensed sources used by the licensee, but excludes background radiation. It also includes radioactive materials remaining at the site as a result of routine or accidental releases of radioactive materials at the site and previous burials at the site, even if those burials were made in accordance with the provisions of Part IV (12VAC5-481-600 et seq.) of this chapter.
"Residual waste" means low-level radioactive waste resulting from processing or decontamination activities that cannot be easily separated into distinct batches attributable to specific waste generators. This waste is attributable to the processor or decontamination facility, as applicable.
"Respiratory protective device" means an apparatus, such as a respirator, used to reduce an individual's intake of airborne radioactive materials.
"Restricted area" means an area, access to which is limited by the licensee or registrant for the purpose of protecting individuals against undue risks from exposure to radiation and radioactive materials. Restricted area does not include areas used as residential quarters, but separate rooms in a residential building may be set apart as a restricted area.
"Reviewing official" means the individual who shall make the trustworthiness and reliability determination of an individual to determine whether the individual may have, or continue to have, unescorted access to the Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive materials that are possessed by the licensee.
"Roentgen" means the special unit of exposure. One roentgen (R) equals 2.58E-4 coulombs per kilogram of air (see "Exposure" and 12VAC5-481-240).
"S-tube" means a tube through which the radioactive source travels when inside a radiographic exposure device.
"Sabotage" means deliberate damage, with malevolent intent, to a Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material, a device that contains a Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material, or the components of the security system.
"Safe haven" means a readily recognizable and readily accessible site at which security is present or from which, in the event of an emergency, the transport crew can notify and wait for the local law-enforcement authorities.
"Sanitary sewerage" means a system of public sewers for carrying off waste water and refuse, but excluding sewage treatment facilities, septic tanks, and leach fields owned or operated by the licensee or registrant.
"Scan" means the complete process of collecting x-ray transmission data for the production of a tomogram. Data can be collected simultaneously during a single scan for the production of one or more tomograms.
"Scan increment" means the amount of relative displacement of the patient with respect to the CT x-ray system between successive scans measured along the direction of such displacement.
"Scan sequence" means a preselected set of two or more scans performed consecutively under preselected CT conditions of operation.
"Scan time" means the period of time between the beginning and end of x-ray transmission data accumulation for a single scan.
"Scattered radiation" means ionizing radiation emitted by interaction of ionizing radiation with matter, the interaction being accompanied by a change in direction of the radiation. Scattered primary radiation means that scattered radiation which has been deviated in direction only by materials irradiated by the useful beam.
"Sealed source" means any radioactive material that is encased in a capsule designed to prevent leakage or escape of any radioactive material.
"Secondary dose monitoring system" means a system which will terminate irradiation in the event of failure of the primary dose monitoring system.
"Security zone" means any temporary or permanent area determined and established by the licensee for the physical protection of Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material.
"Seismic area" means any area where the probability of a horizontal acceleration in rock of more than 0.3 times the acceleration of gravity in 250 years is greater than 10%, as designated by the United States Geological Survey.
"Self-contained breathing apparatus" or "SCBA" means an atmosphere-supplying respirator for which the breathing air source is designed to be carried by the user.
"Shadow tray" means a device attached to the radiation head to support auxiliary beam blocking material.
"Shallow dose equivalent" or "Hs," which applies to the external exposure of the skin or an extremity, means the dose equivalent at a tissue depth of 0.007 centimeter (7 mg/cm2).
"Shielded position" means the location within the radiographic exposure device or storage container which, by manufacturer's design, is the proper location for storage of the sealed source.
"Shielded-room radiography" means industrial radiography conducted in a room shielded so that radiation levels at every location on the exterior meet the limitations specified in 12VAC5-481-640.
"Shipper" means the licensed entity (i.e., the waste generator, waste collector, or waste processor) who offers low-level radioactive waste for transportation, typically consigning this type of waste to a licensed waste collector, waste processor, or land disposal facility operator.
"Shipping paper" means NRC Form 540 and, if required, NRC Form 540A, which includes the information required by the U.S. Department of Transportation in 49 CFR Part 172.
"Shutter" means a device attached to the tube housing assembly which can intercept the entire cross sectional area of the useful beam and which has a lead equivalency not less than that of the tube housing assembly.
"SI" means the abbreviation for the International System of Units.
"SID" (See "Source-image receptor distance").
"Sievert" or "Sv" means the SI unit of any of the quantities expressed as dose equivalent. The dose equivalent in sievert is equal to the absorbed dose in gray multiplied by the quality factor (1 Sv = 100 rem).
"Simulator" or "radiation therapy simulation system" means any x-ray system intended for localizing the volume to be exposed during radiation therapy and reproducing the position and size of the therapeutic irradiation field.
"Single tomogram system" means a CT x-ray system that obtains x-ray transmission data during a scan to produce a single tomogram.
"Site area emergency" means events may occur, are in progress, or have occurred that could lead to a significant release of radioactive material and that could require a response by offsite response organizations to protect persons offsite.
"Site boundary" means that line beyond which the land or property is not owned, leased, or otherwise controlled by the licensee.
"Site closure and stabilization" means those actions that are taken upon completion of operations that prepare the disposal site for custodial care and that assure that the disposal site will remain stable and will not need ongoing active maintenance.
"Source" means the focal spot of the x-ray tube.
"Source assembly" means an assembly that consists of the sealed source and a connector that attaches the source to the control cable. The source assembly may include a ballstop to secure the source in the shielded position.
"Source changer" means a device designed and used for replacement of sealed sources in radiographic exposure devices, including those source changers also used for transporting and storage of sealed sources.
"Source holder" means a housing or assembly into which a radioactive source is placed for the purpose of facilitating the handling and use of the source in well-logging operations.
"Source-image receptor distance" means the distance from the source to the center of the input surface of the image receptor.
"Source material" means:
1. Uranium or thorium, or any combination thereof, in any physical or chemical form; or
2. Ores that contain by weight one-twentieth of 1.0% (0.05%) or more of uranium, thorium or any combination of uranium and thorium. Source material does not include special nuclear material.
"Source of radiation" means any radioactive material or any device or equipment emitting, or capable of producing, radiation.
"Source-skin distance" or "SSD" means the distance from the source to the center of the entrant x-ray field in the plane tangent to the patient's skin surface.
"Source traceability" means the ability to show that a radioactive source has been calibrated either by the national standards laboratory of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, or by a laboratory that participates in a continuing measurement quality assurance program with National Institute of Standards and Technology or other equivalent national or international program.
"Special form radioactive material" means radioactive material that satisfies the following conditions:
1. It is either a single solid piece or is contained in a sealed capsule that can be opened only by destroying the capsule;
2. The piece or capsule has at least one dimension not less than five millimeters (0.2 in.); and
3. It satisfies the requirements of 10 CFR 71.75. A special form encapsulation designed in accordance with the NRC requirements of 10 CFR 71.4 in effect on June 30, 1983 (see 10 CFR Part 71, revised as of January 1, 1983), and constructed before July 1, 1985; a special form encapsulation designed in accordance with the requirements of 10 CFR 71.4 in effect on March 31, 1996 (see 10 CFR Part 71, revised as of January 1, 1996), and constructed before April 1, 1998; and special form material that was successfully tested before September 10, 2015, in accordance with the requirements of 10 CFR 71.75(d) in effect before September 10, 2015, may continue to be used. Any other special form encapsulation must meet requirements of this definition.
"Special nuclear material" means:
1. Plutonium, uranium-233, uranium enriched in the isotope 233 or in the isotope 235, and any other material the NRC, pursuant to the provisions of § 51 of the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, as amended, (42 USC § 2071) determines to be special nuclear material, but does not include source material; or
2. Any material artificially enriched by any of the foregoing but does not include source material.
"Special nuclear material in quantities not sufficient to form a critical mass" means uranium enriched in the isotope U-235 in quantities not exceeding 350 grams of contained U-235; uranium-233 in quantities not exceeding 200 grams; plutonium in quantities not exceeding 200 grams; or any combination of them in accordance with the following formula: For each kind of special nuclear material, determine the ratio between the quantity of that special nuclear material and the quantity specified above for the same kind of special nuclear material. The sum of such ratios for all of the kinds of special nuclear material in combination shall not exceed 1. For example, the following quantities in combination would not exceed the limitation and are within the formula:
(175 grams contained U235/350) + (50 grams U – 233/200) + (50 grams Pu/200) = 1
"Specific activity of a radionuclide" means the radioactivity of a radionuclide per unit mass of that nuclide. The specific activity of a material in which the radionuclide is essentially uniformly distributed is the radioactivity per unit mass of the material.
"Spot film" means a radiograph that is made during a fluoroscopic examination to permanently record conditions that exist during that fluoroscopic procedure.
"Spot-film device" means a device intended to transport or position a radiographic image receptor between the x-ray source and fluoroscopic image receptor. It includes a device intended to hold a cassette over the input end of an image intensifier for the purpose of making a radiograph.
"Stability" means structural stability.
"State inspector" means an employee of the Virginia Department of Health designated to perform those duties or functions assigned the Radiological Health Program.
"Stationary beam radiation therapy" means radiation therapy without displacement of one or more mechanical axes relative to the patient during irradiation.
"Stationary x-ray equipment" (See "x-ray equipment").
"Stochastic effect" means a health effect that occurs randomly and for which the probability of the effect occurring, rather than its severity, is assumed to be a linear function of dose without threshold. Hereditary effects and cancer incidence are examples of stochastic effects. For purposes of this chapter, "probabilistic effect" is an equivalent term.
"Storage" means a condition in which a device or source is not being used for an extended period of time, and has been made inoperable.
"Storage area" means any location, facility, or vehicle that is used to store and secure a radiographic exposure device, a radiation machine, or a storage container when it is not used for radiographic operations. Storage areas are locked or have a physical barrier to prevent accidental exposure, tampering, or unauthorized removal of the device, machine, or container.
"Storage container" means a device in which sealed sources or radiation machines are secured and stored.
"Stray radiation" means the sum of leakage and scattered radiation.
"Subsurface tracer study" means the release of a substance tagged with radioactive material for the purpose of tracing the movement or position of the tagged substance in the well-bore or adjacent formation.
"Supplied-air respirator," "airline respirator," or "SAR" means an atmosphere-supplying respirator for which the source of breathing air is not designed to be carried by the user.
"Surface contaminated object" or "SCO" means a solid object that is not itself classed as radioactive material, but that has radioactive material distributed on any of its surfaces. An SCO must be in one of two groups with surface activity not exceeding the following limits:
1. SCO-I: A solid object on which:
a. The nonfixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm², or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm², does not exceed four becquerel per cm² (1 E-04 µCi/cm²) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 0.4 becquerel per cm² (1 E-05 µCi/cm²) for all other alpha emitters;
b. The fixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm², or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm², does not exceed 4 E+04 becquerel per cm² (1.0 µCi/cm²) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 4 E+03 becquerel per cm² (0.1 µCi/cm²) for all other alpha emitters; and
c. The nonfixed contamination plus the fixed contamination on the inaccessible surface averaged over 300 cm², or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm², does not exceed 4 E+04 becquerel per cm² (1 µCi/cm²) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 4 E+03 Becquerel per cm² (0.1 µCi/cm²) for all other alpha emitters.
2. SCO-II: A solid object on which the limits for SCO-I are exceeded and on which:
a. The nonfixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm², or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm², does not exceed 400 becquerel per cm² (1 E-02 µCi/cm²) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters or 40 becquerel per cm² (1 E-03 µCi/cm²) for all other alpha emitters;
b. The fixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm², or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm², does not exceed 8 E+05 becquerel per cm² (20 µCi/cm²) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 8 E+04 becquerel per cm² (2 µCi/cm²) for all other alpha emitters; and
c. The nonfixed contamination plus the fixed contamination on the inaccessible surface averaged over 300 cm², or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm², does not exceed 8 E+05 becquerel per cm² (20 µCi/cm²) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 8 E+04 becquerel per cm² (2 µCi/cm²) for all other alpha emitters.
"Surveillance" means monitoring and observation of the disposal site for purposes of visual detection of need for maintenance, custodial care, evidence of intrusion, and compliance with other license and regulatory requirements.
"Survey" means an evaluation of the radiological conditions and potential hazards incident to the production, use, transfer, release, disposal, or presence of radioactive material or other sources of radiation. When appropriate, such an evaluation includes a physical survey of the location of radioactive material and measurements or calculations of levels of radiation, or concentrations or quantities of radioactive material present.
"Tabletop, stationary" means a tabletop that, when assembled for use, is incapable of movement with respect to its supporting structure within the plane of the tabletop.
"Target" means that part of an x-ray tube or accelerator onto which a beam of accelerated particles is directed to produce ionizing radiation or other particles.
"Target-skin distance" or "TSD" means the distance measured along the beam axis from the center of the front surface of the x-ray target or electron virtual source, or both, to the surface of the irradiated object or patient.
"Technologically enhanced naturally occurring radioactive material" or "TENORM" means, as used in Part XVI (12VAC5-481-3460 et seq.) of this chapter, naturally occurring radionuclides whose concentrations are increased by or as a result of past or present human practices. TENORM does not include background radiation or the natural radioactivity of rocks or soils. TENORM does not include uranium or thorium in "source material" as defined in the AEA and NRC regulations.
"Technique factors" means the following conditions of operation:
1. For capacitor energy storage equipment, peak tube potential in kilovolts (kV) and quantity of charge in milliampere-seconds (mAs);
2. For field emission equipment rated for pulsed operation, peak tube potential in kilovolts (kV), and number of x-ray pulses;
3. For CT equipment designed for pulsed operation, peak tube potential in kilovolts (kV), scan time in seconds, and either tube current in milliamperes (mA), x-ray pulse width in seconds, and the number of x-ray pulses per scan, or the product of tube current, x-ray pulse width, and the number of x-ray pulses in milliampere-seconds (mAs);
4. For CT equipment not designed for pulsed operation, peak tube potential in kilovolts (kV), and either tube current in milliamperes (mA) and scan time in seconds, or the product of tube current and exposure time in milliampere-seconds (mAs) and the scan time when the scan time and exposure time are equivalent; and
5. For all other equipment, peak tube potential in kilovolts (kV), and either tube current in milliamperes (mA) and exposure time in seconds, or the product of tube current and exposure time in milliampere-seconds (mAs).
"Telemetric position monitoring system" means a data transfer system that captures information by either instrumentation or measuring devices, or both, about the location and status of a transport vehicle or package between the departure and destination locations.
"Teletherapy physicist" means an individual identified as a qualified teletherapy physicist on an agency license.
"Teletherapy" means therapeutic irradiation in which the source of radiation is at a distance from the body.
"Temporary job site" means any location where industrial radiography, wireline service, well-logging, portable gauge or x-ray fluorescence use is performed and where licensed material may be stored other than those locations of use authorized on the license.
"Tenth-value layer" or "TVL" means the thickness of a specified material that attenuates x-radiation or gamma radiation to an extent such that the air kerma rate, exposure rate, or absorbed dose rate is reduced to one-tenth of the value measured without the material at the same point.
"Test" means the process of verifying compliance with an applicable regulation.
"Therapeutic radiation machine" means x-ray or electron-producing equipment designed and used for external beam radiation therapy. For the purpose of this chapter, devices used to administer electronic brachytherapy shall also be considered therapeutic radiation machines.
"These regulations" mean all parts of this chapter.
"Tight-fitting facepiece" means a respiratory inlet covering that forms a complete seal with the face.
"Tomogram" means the depiction of the x-ray attenuation properties of a section through the body.
"Tomographic plane" means that geometric plane that is identified as corresponding to the output tomogram.
"Tomographic section" means the volume of an object whose x-ray attenuation properties are imaged in a tomogram.
"Total effective dose equivalent" or "TEDE" means the sum of the effective dose equivalent for external exposures and the committed effective dose equivalent for internal exposures.
"Total organ dose equivalent" or "TODE" means the sum of the deep dose equivalent and the committed dose equivalent to the organ receiving the highest dose as described in 12VAC5-481-1040.
"Traceable to a National Standard" (See "Instrument traceability" or "Source traceability").
"Transfer" means, as used in Part XVI (12VAC5-481-3460 et seq.) of this chapter, the physical relocation of NORM containing materials not directly associated with commercial distribution within a business's operation or between general or specific licensees. This term does not include a change in legal title to NORM containing materials that does not involve physical movement of those materials.
"Transport container" means a package that is designed to provide radiation safety and security when sealed sources are transported and that meets all applicable requirements of the U.S. Department of Transportation.
"Transport index" or "TI" means the dimensionless number, rounded up to the next tenth, placed on the label of a package to designate the degree of control to be exercised by the carrier during transportation. The transport index is the number determined by multiplying the maximum radiation level in millisievert (mSv) per hour at one meter (3.3 feet) from the external surface of the package by 100 (equivalent to the maximum radiation level in millirem per hour at one meter (3.3 feet)).
"Treatment site" means the correct anatomical description of the area intended to receive a radiation dose, as described in a written directive.
"Tribal official" means the highest ranking individual that represents tribal leadership, such as the chief, president, or tribal council leadership.
"Tritium neutron generator target source" means a tritium source used within a neutron generator tube to produce neutrons for use in well-logging applications.
"Trustworthiness and reliability" means characteristics of an individual considered dependable in judgment, character, and performance, such that unescorted access to Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material by that individual does not constitute an unreasonable risk to the public health and safety or security. A determination of trustworthiness and reliability for this purpose is based upon the results from a background investigation.
"Tube" means an x-ray tube, unless otherwise specified.
"Tube housing assembly" means the tube housing with tube installed. It includes high-voltage or filament transformers and other appropriate elements when such are contained within the tube housing.
"Tube rating chart" means the set of curves which specify the rated limits of operation of the tube in terms of the technique factors.
"Type A quantity" means a quantity of radioactive material, the aggregate radioactivity of which does not exceed A1 for special form radioactive material or A2 for normal form radioactive material, where A1 and A2 are given in Table 1 of 12VAC5-481-3770 F or may be determined by procedures described in 12VAC5-481-3770 A through E.
"Type B quantity" means a quantity of radioactive material greater than a Type A quantity.
"Underwater irradiator" means an irradiator in which the sources always remain shielded under water and humans do not have access to the sealed sources or the space subject to irradiation without entering the pool.
"Underwater radiography" means radiographic operations performed when the radiographic exposure device or radiation machine or related equipment are beneath the surface of the water.
"Unescorted access" means solitary access to an aggregated Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material or the devices that contain the material.
"Uniform Low-Level Radioactive Waste Manifest" or "uniform manifest" means the combination of NRC Forms 540 and 541, and, if necessary, 542, and their respective continuation sheets as needed, or equivalent.
"Unirradiated uranium" means uranium containing not more than 2 x 103 Bq of plutonium per gram of uranium-235, not more than 9 x 106 Bq of fission products per gram of uranium-235, and not more than 5 x 10-3 g of uranium-236 per gram of uranium-235.
"Unrefined and unprocessed ore" means ore in its natural form prior to any processing, such as grinding, roasting, beneficiating, or refining. Processing does not include sieving or encapsulating of ore or preparation of samples for laboratory analysis.
"Unrestricted area" means an area, access to which is neither limited nor controlled by the licensee or registrant. For purposes of these regulations, "uncontrolled area" is an equivalent term.
"Uranium - natural, depleted, enriched"
1. "Natural uranium" means uranium (which may be chemically separated) with the naturally occurring distribution of uranium isotopes, which is approximately 0.711 weight percent uranium-235, and the remainder by weight essentially uranium-238.
2. "Depleted uranium" means uranium containing less uranium-235 than the naturally occurring distribution of uranium isotopes.
3. "Enriched uranium" means uranium containing more uranium-235 than the naturally occurring distribution of uranium isotopes.
"Uranium sinker bar" means a weight containing depleted uranium used to pull a logging tool down toward the bottom of a well.
"Useful beam" means the radiation that passes through the tube housing port and the aperture of the beam-limiting device when the exposure switch or timer is activated.
"User seal check" or "fit check" means an action conducted by the respirator user to determine if the respirator is properly seated to the face. Examples include negative pressure check, positive pressure check, irritant smoke check, or isoamyl acetate check.
"Variable-aperture beam-limiting device" means a beam-limiting device which has capacity for stepless adjustment of the x-ray field size at a given SID.
"Very high radiation area" means an area, accessible to individuals, in which radiation levels from radiation sources external to the body could result in an individual receiving an absorbed dose in excess of five Gy (500 rad) in one hour at one meter from a source of radiation or one meter from any surface that the radiation penetrates.
"Virtual simulator" means a computed tomography (CT) unit used in conjunction with relevant software that recreates the treatment machine and that allows import, manipulation, display, and storage of images from CT or other imaging modalities, or both.
"Virtual source" means a point from which radiation appears to originate.
"Visible area" means that portion of the input surface of the image receptor over which incident x-ray photons are producing a visible image.
"Visiting authorized user" means an authorized user who is not identified on the license of the licensee being visited.
"Waste" means those low-level radioactive wastes containing source, special nuclear, or byproduct material that are acceptable for disposal in a land disposal facility. For the purposes of this definition, low-level radioactive waste means radioactive waste not classified as high-level radioactive waste, transuranic waste, spent nuclear fuel, or byproduct material as defined in subdivisions 2, 3, and 4 of the definition of byproduct material.
"Waste collector" means an entity, operating under a specific license, whose principal purpose is to collect and consolidate waste generated by others, and to transfer this waste, without processing or repackaging the collected waste, to another licensed waste collector, licensed waste processor, or licensed land disposal facility.
"Waste description" means the physical, chemical and radiological description of a low-level radioactive waste as called for on NRC Form 541.
"Waste generator" means an entity, operating under a license, that (i) possesses any material or component that contains radioactivity or is radioactively contaminated for which the licensee foresees no further use, and (ii) transfers this material or component to a licensed land disposal facility or to a licensed waste collector or processor for handling or treatment prior to disposal. A licensee performing processing or decontamination services may be a "waste generator" if the transfer of low-level radioactive waste from its facility is defined as "residual waste."
"Waste handling licensees" mean persons licensed to receive and store radioactive wastes prior to disposal or persons licensed to dispose of radioactive waste.
"Waste processor" means an entity, operating under a specific license, whose principal purpose is to process, repackage, or otherwise treat low-level radioactive material or waste generated by others prior to eventual transfer of waste to a licensed low-level radioactive waste land disposal facility.
"Waste type" means a waste within a disposal container having a unique physical description (i.e., a specific waste descriptor code or description; or a waste sorbed on or solidified in a specifically defined media).
"Wedge filter" means a filter that effects continuous change in transmission over all or a part of the useful beam.
"Week" means seven consecutive days starting on Sunday.
"Weighting factor" or "wT" for an organ or tissue (T) means the proportion of the risk of stochastic effects resulting from irradiation of that organ or tissue to the total risk of stochastic effects when the whole body is irradiated uniformly. For calculating the effective dose equivalent, the values of wT are:
| Organ Dose Weighting Factors |
| Organ or Tissue | wT |
| Gonads | 0.25 |
| Breast | 0.15 |
| Red bone marrow | 0.12 |
| Lung | 0.12 |
| Thyroid | 0.03 |
| Bone surfaces | 0.03 |
| Remainder | 0.30a/ |
| Whole Body | 1.00b/ |
| a/0.30 results from 0.06 for each of five "remainder" organs, excluding the skin and the lens of the eye, that receive the highest doses. |
| b/For the purpose of weighting the external whole body dose for adding it to the internal dose, a single weighting factor, wT = 1.0, has been specified. The use of other weighting factors for external exposure will be approved on a case-by-case basis until such time as specific guidance is issued. |
"Well-bore" means a drilled hole in which wireline service operations or subsurface tracer studies are performed.
"Well-logging" means all operations involving the lowering and raising of measuring devices or tools that may contain sources of radiation into well-bores or cavities for the purpose of obtaining information about the well or adjacent formations.
"Whole body" means, for purposes of external exposure, head, trunk including male gonads, arms above the elbow, or legs above the knee.
"Wireline" means a cable containing one or more electrical conductors that is used to lower and raise logging tools in the well-bore.
"Wireline service operation" means any evaluation or mechanical service that is performed in the well-bore using devices on a wireline.
"Worker" means an individual engaged in work under a license or registration issued by the agency and controlled by a licensee or registrant but does not include the licensee or registrant.
"Working level" or "WL" means any combination of short-lived radon daughters in one liter of air that will result in the ultimate emission of 1.3E+5 MeV of potential alpha particle energy. The short-lived radon daughters of radon-222 are polonium-218, lead-214, bismuth-214, and polonium-214; and those of radon-220 are polonium-216, lead-212, bismuth-212, and polonium-212.
"Working level month" or "WLM" means an exposure to one working level for 170 hours. Two thousand working hours per year divided by 12 months per year is approximately equal to 170 hours per month.
"Written directive" means an order in writing for a specific patient, dated and signed by an authorized user prior to the administration of a radiopharmaceutical or radiation, except as specified in subdivision 6 of this definition, containing the following information: an authorized user's written order for the administration of radioactive material, radiation from radioactive material, or radiation from a radiation producing machine to a specific patient or human research subject.
1. For any administration of quantities greater than 1.11 megabecquerels (30 mCi) of sodium iodide I-125 or I-131: the radionuclide, and dosage;
2. For a therapeutic administration of a radiopharmaceutical other than sodium iodide I-125 or I-131: the radiopharmaceutical, dosage, and route of administration;
3. For gamma stereotactic radiosurgery: target coordinates, collimator size, plug pattern, and total dose;
4. For teletherapy: the total dose, dose per fraction, treatment site, and overall treatment period;
5. For high-dose-rate remote afterloading brachytherapy: the radionuclide, treatment site, and total dose; or
6. For all other brachytherapy,
a. Prior to implantation: the radionuclide, number of sources, and source strengths; and
b. After implantation but prior to completion of the procedure: the radionuclide, treatment site, and total source strength and exposure time (or, equivalently, the total dose).
"X-ray control" means a device that controls input power to the x-ray high-voltage generator or the x-ray tube. It includes equipment such as timers, phototimers, automatic brightness stabilizers, and similar devices, which control the technique factors of an x-ray exposure.
"X-ray exposure control" means a device, switch, button or other similar means by which an operator initiates or terminates the radiation exposure. The x-ray exposure control may include such associated equipment as timers and back-up timers.
"X-ray equipment" means an x-ray system, subsystem, or component thereof. Types of x-ray equipment are as follows:
1. "Mobile x-ray equipment" means x-ray equipment mounted on a permanent base with wheels or casters for moving while completely assembled.
2. "Portable x-ray equipment" means x-ray equipment designed to be hand-carried.
3. "Stationary x-ray equipment" means x-ray equipment that is installed in a fixed location.
"X-ray field" means that area of the intersection of the useful beam and any one of the sets of planes parallel to and including the plane of the image receptor, whose perimeter is the locus of points at which the AKR is one-fourth of the maximum in the intersection.
"X-ray high-voltage generator" means a device that transforms electrical energy from the potential supplied by the x-ray control to the tube operating potential. The device may also include means for transforming alternating current to direct current, filament transformers for the x-ray tubes, high-voltage switches, electrical protective devices, and other appropriate elements.
"X-ray system" means an assemblage of components for the controlled production of x-rays. It includes minimally an x-ray high-voltage generator, an x-ray control, a tube housing assembly, a beam-limiting device, and the necessary supporting structures. Additional components that function with the system are considered integral parts of the system.
"X-ray table" means a patient support device with its patient support structure (tabletop) interposed between the patient and the image receptor during radiography or fluoroscopy. This includes, but is not limited to, any stretcher equipped with a radiolucent panel and any table equipped with a cassette tray (or bucky), cassette tunnel, fluoroscopic image receptor, or spot-film device beneath the tabletop.
"X-ray tube" means any electron tube that is designed for the conversion of electrical energy into x-ray energy.
"Year" means the period of time beginning in January used to determine compliance with the provisions of this chapter. The licensee or registrant may change the starting date of the year used to determine compliance by the licensee or registrant provided that the change is made at the beginning of the year. If a licensee or registrant changes in a year, the licensee or registrant shall assure that no day is omitted or duplicated in consecutive years.
12VAC5-481-2970. Exemptions.
A. Common and contract carriers, freight forwarders, and warehouse workers that are subject to the requirements of the United States Department of Transportation (DOT) in 49 CFR Part 170 through 49 Part CFR 189 or the United States Postal Service in the Postal Service Domestic Mail Manual (DMM), Section C-023.9.0, and the United States Postal Service, are exempt from the requirements of this part to the extent that they transport or store radioactive material in the regular course of their carriage for others or storage incident thereto. Common and contract carriers that are not subject to the requirements of the DOT or United States Postal Service are subject to 12VAC5-481-2960 and other applicable requirements of these regulations.
B. A licensee is exempt from all the requirements of this part with respect to shipment or carriage of the following low-level materials:
1. Natural material and ores containing naturally occurring radionuclides that are either in their natural state, or have only been processed for purposes other than the extraction of the radionuclides, and that are not intended to be processed for use of these radionuclides, provided the activity concentration of the material does not exceed 10 times the values specified in Table 2 or Table 3 of 12VAC5-481-3770.
2. Materials for which the activity concentration is not greater than the activity concentration values specified in Table 2 or Table 3 of 12VAC5-481-3770, or for which the consignment activity is not greater than the limit for an exempt consignment found in Table 2 or Table 3 of 12VAC5-481-3770.
3. Nonradioactive solid objects with radioactive substances present on any surfaces in quantities not in excess of the levels cited in the definition of "contamination" in 12VAC5-481-10.
C. Fissile material meeting one of the following requirements are exempt from classification as fissile material and from the fissile material package standards of 10 CFR 71.55 and 10 CFR 71.59, but are subject to all other requirements of 10 CFR 71, except as noted.
1. Individual package containing two grams or less fissile material.
2. Individual or bulk packaging containing 15 grams or less of fissile material provided the package has at least 200 grams of solid nonfissile material for every gram of fissile material. Lead, beryllium, graphite, and hydrogenous material enriched in deuterium may be present in the package but must not be included in determining the required mass for solid nonfissile material.
3. Low concentrations of solid fissile material commingled with solid nonfissile material, provided that there is at least 2,000 grams of solid nonfissile material for every gram of fissile material, and there is no more than 180 grams of fissile material distributed within 360 kg of contiguous nonfissile material. Lead, beryllium, graphite, and hydrogenous material enriched in deuterium may be present in the package but must not be included in determining the required mass of solid nonfissile material.
4. Uranium enriched in uranium-235 to a maximum of 1.0% by weight, and with total plutonium and uranium-233 content of up to 1.0% of the mass of uranium-235, provided that the mass of any beryllium, graphite, and hydrogenous material enriched in deuterium constitutes less than 5.0% of the uranium mass, and that the fissile material is distributed homogeneously and does not form a lattice arrangement within the package.
5. Liquid solutions of uranyl nitrate enriched in uranium-235 to a maximum of 2.0% by mass, with a total plutonium and uranium-233 content not exceeding 0.002% of the mass of uranium, and with a minimum nitrogen to uranium atomic ratio (N/U) of 2. The material must be contained in at least a DOT Type A package.
6. Packages containing, individually, a total plutonium mass of not more than 1,000 grams, of which not more than 20% by mass may consist of plutonium-239, plutonium-241, or any combination of these radionuclides.
D. Any physician licensed by the Commonwealth of Virginia to dispense drugs in the practice of medicine is exempt from this section with respect to transport by the physician of radioactive material for use in the practice of medicine provided the physician is an authorized user under Part VII (12VAC5-481-1660 et seq.).
12VAC5-481-3000. General license: NRC-approved packages.
A. A general license is hereby issued to any licensee to transport, or to deliver to a carrier for transport, licensed material in a package for which a license, certificate of compliance (CoC), or other approval has been issued by the NRC. This general license applies only to a licensee who has a quality assurance program approved by the agency as satisfying the provisions of 12VAC5-481-3130.
B. This general license applies only to a licensee who:
1. Has a copy of the license, CoC, or other approval by the NRC of the package and has the drawings and other documents referenced in the approval relating to the use and maintenance of the packaging and to the actions to be taken prior to shipment;
2. Complies with the terms and conditions of the license, certificate, or other approval by the NRC, as applicable, and the applicable requirements of Part XIII (12VAC5-481-2950 et seq.) of this chapter;
3. Prior to the licensee's first use of the package, submits in writing to the agency NRC: ATTN: Document Control Desk, Director, Division of Spent Fuel Storage and Transportation, Office of Nuclear Material Safety and Safeguards, using an appropriate method listed in 10 CFR 71.1(a), the licensee's name and license number and the package identification number specified in the package approval in accordance with 12VAC5-481-150; and
4. Has a quality assurance program that complies with 12VAC5-481-3130.
C. The general license in subsection A of this section applies only when the package approval authorizes use of the package under this general license.
D. For a Type B or fissile material package, the design of which was approved by the NRC before April 1, 1996, the general license is subject to the additional restrictions of 12VAC5-481-3010.
Article 5
Quality Assurance
12VAC5-481-3130. Quality assurance.
A. Quality assurance requirements apply to the design, purchase, fabrication, handling, shipping, storing, cleaning, assembly, inspection, testing, operation, maintenance, repair, and modification of components of packaging that are important to safety. Quality assurance comprises all those planned and systematic actions necessary to provide adequate confidence that a system or component will perform satisfactorily in service. Quality assurance includes quality control, which comprises those quality assurance actions related to control of the physical characteristics and quality of the material or component to predetermined requirements. The licensee is responsible for the quality assurance requirements as they apply to design, fabrication, testing, and modification of packaging. Each licensee is responsible for the quality assurance provision that applies to its use of packaging for the shipment of licensed material subject to this chapter.
B. Each licensee shall establish, maintain, and execute a quality assurance program satisfying each of that applicable criteria of this section, 10 CFR Part 71 Subpart H and satisfying any specific provisions that are applicable to the licensee's activities including procurement of packaging. The licensee shall execute the applicable criteria in a graded approach to an extent that is commensurate with the quality assurance requirement's importance to safety.
C. Before the use of any package for the shipment of licensed material subject to this rule, each licensee shall obtain approval of its quality assurance program. Using an appropriate method, each licensee shall file a description of its quality assurance program, including a discussion of which requirements of this section are applicable and how they will be satisfied by submitting the description to the agency.
D. A program for transport container inspection and maintenance limited to radiographic exposure devices, source changers, or packages transporting these devices and meeting the requirements of 12VAC5-481-1270 or equivalent NRC or agreement state requirement, is deemed to satisfy the requirements of 12VAC5-481-3000 and subsection B of this section.
E. The licensee shall be responsible for the establishment and execution of the quality assurance program. The licensee may delegate to others, such as contractors, agents, or consultants, the work of establishing and executing the quality assurance program, or any part of the quality assurance program, but shall retain responsibility for the program. The licensee shall clearly establish and delineate, in writing, the authority and duties of persons and organizations performing activities affecting the safety-related functions of structures, systems, and components. These activities include performing the functions associated with attaining quality objectives and the quality assurance functions. While the term licensee is used in these criteria, the requirements are applicable to whatever design, fabrication, assembly, and testing of the package is accomplished with respect to a package before the time a package is issued.
F. The quality assurance functions are:
1. Assuring that an appropriate quality assurance program is established and effectively executed; and
2. Verifying, by procedures such as checking, auditing, and inspection, that activities affecting the safety-related functions have been performed correctly.
G. The persons and organizations performing quality assurance functions must have sufficient authority and organizational freedom to:
1. Identify quality problems;
2. Initiate, recommend, or provide solutions; and
3. Verify implementation of solutions.
H. Changes to the quality assurance program.
1. Each quality assurance program approval holder shall submit a description of a proposed change to its agreement state agency approved quality assurance program that will reduce commitments in the program description as approved by the agreement state agency. The quality assurance program approval holder shall not implement the change before receiving approval.
The description of a proposed change to the agreement state agency approved quality assurance program must identify the change, the reason for the change, and the basis for concluding that the revised program incorporating the change continues to satisfy the applicable requirements of this section.
2. Each quality assurance program approval holder may change a previously approved quality assurance program without prior agreement state agency approval if the change does not reduce the commitments in the quality assurance program previously approved by the agreement state agency. Changes to the quality assurance program that do not reduce the commitments shall be submitted to the agreement state agency every 24 months. In addition to quality assurance program changes involving administrative improvements and clarifications, spelling corrections, and nonsubstantive changes to punctuation or editorial items, the following changes are not considered reductions in commitment:
a. The use of a quality assurance standard approved by the agreement state agency that is more recent than the quality assurance standard in the licensee's current quality assurance program at the time of the change;
b. The use of generic organizational position titles that clearly denote the position function, supplemented as necessary by descriptive text, rather than specific titles, provided that there is no substantive change to either the functions of the position or reporting requirements;
c. The use of generic organization charts to indicate functional relationships, authorities, and responsibilities, or alternatively, the use of descriptive text, provided that there is no substantive change to the functional relationships, authorities, or responsibilities;
d. The elimination of quality assurance program information that duplicates language in quality assurance regulatory guides and quality assurance standards to which the quality assurance program approval holder has committed to on record; and
e. Organizational revisions that ensure that persons and organizations performing quality assurance functions continue to have the requisite authority and organizational freedom, including independence from cost and schedule when opposed to safety considerations.
3. Each quality assurance program approval holder shall maintain records of quality assurance program changes.
I. The licensee shall maintain sufficient written records to describe the activities affecting quality. These records must include the changes to the quality assurance program as required by subsection H of this section, the instructions, procedures, and drawings required by this section to prescribe quality assurance activities, and closely related specifications such as required qualifications of personnel, procedures, and equipment. The records must include the instructions or procedures that establish a records retention program that is consistent with applicable regulations and designates factors such as duration, location, and assigned responsibility. The licensee shall retain these records for three years beyond the date when the licensee last engaged in the activity for which the quality assurance program was developed. If any portion of the quality assurance program, written procedures or instructions is superseded, the licensee shall retain the superseded material for three years after it is superseded.
VA.R. Doc. No. R18-5355; Filed February 13, 2018, 11:05 a.m.
TITLE 18. PROFESSIONAL AND OCCUPATIONAL LICENSING
VA.R. Doc. No. R16-4544; Filed February 7, 2018, 10:57 a.m.
TITLE 18. PROFESSIONAL AND OCCUPATIONAL LICENSING
VA.R. Doc. No. R17-05; Filed February 5, 2018, 5:23 p.m.
TITLE 18. PROFESSIONAL AND OCCUPATIONAL LICENSING
VA.R. Doc. No. R18-5412; Filed February 13, 2018, 1:42 p.m.
TITLE 18. PROFESSIONAL AND OCCUPATIONAL LICENSING
VA.R. Doc. No. R18-5412; Filed February 13, 2018, 1:42 p.m.
TITLE 21. SECURITIES AND RETAIL FRANCHISING
VA.R. Doc. No. R18-5246; Filed February 6, 2018, 5:18 p.m.